ClebschGordan
ClebschGordan[{j1,m1},{j2,m2},{j,m}]
gives the Clebsch–Gordan coefficient for the decomposition of ![]() in terms of
in terms of ![]() .
.
Details
- The Clebsch–Gordan coefficients vanish except when
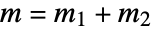 and the
and the 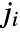 satisfy a triangle inequality.
satisfy a triangle inequality. - The parameters of ClebschGordan can be integers, half‐integers, or symbolic expressions.
- The Wolfram Language uses the standard conventions of Edmonds for the phase of the Clebsch–Gordan coefficients.
- The Clebsch–Gordan coefficients and 3‐
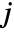 symbols in the Wolfram Language satisfy the relation
symbols in the Wolfram Language satisfy the relation 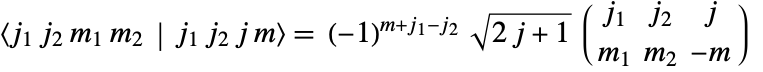 .
.
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (2)
ClebschGordan works with integer and half‐integer arguments:
For symbolic input ClebschGordan evaluates to ThreeJSymbol:
Applications (3)
Plot Clebsch–Gordan coefficients as a function of ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Decompose a spherical harmonic into a sum of products of two spherical harmonics:
Apply angular momentum operators to spherical harmonics:
Properties & Relations (2)
Possible Issues (1)
A message is issued and the result of 0 is returned when ![]() :
:
Text
Wolfram Research (1991), ClebschGordan, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ClebschGordan.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1991. "ClebschGordan." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ClebschGordan.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1991). ClebschGordan. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ClebschGordan.html