TransformColumns
TransformColumns[tab,ncolf]
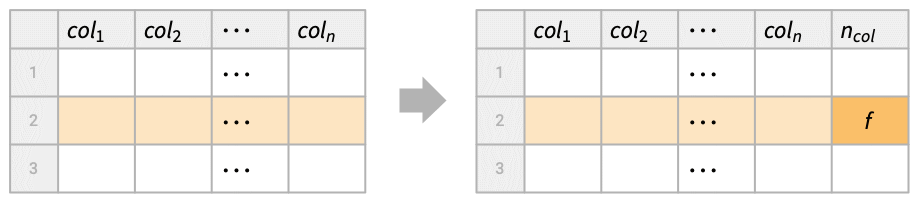
adds a new column with name ncol by transforming the tabular data tab using the function f applied to each row.
TransformColumns[tab,{ncol1f1,ncol2f2,…}]
adds several new columns ncoli by successively applying the functions fi to each row.
TransformColumns[transfs]
represents an operator form of TransformColumns that can be applied to tabular data.
Details and Options
- TransformColumns is typically used to add new columns or modify existing columns, keeping the rest.
- Possible forms of tabular data tab include:
-
Tabular[…] type-consistent tabular data Dataset[…] general hierarchical data {assoc1,assoc2,…} list of associations with common keys matrix matrix of values - If the column ncoli already exists, it is replaced with the newly created one. Otherwise, a new column is added after the existing ones.
- TransformColumns[tab,{col,ncolf}] adds a new column named ncol after the existing column col, instead of appending it at the end.
- For tabular data atab without column keys, TransformColumns[atab,{f1,f2,…,fn}] appends n new anonymous columns by successively applying the functions fi to each row.
- Functions fi are applied to individual rows of the input tabular data tab, with the row being an association <col1val1,…> if tab has column keys or a list {val1,…} if tab does not have column keys.
- When several functions are used, TransformColumns[tab,{…}] is effectively equivalent to Fold[TransformColumns,tab,{…}], allowing each function to access the columns previously added.
- The syntax colNothing can be used to remove the existing column named col. »
- TransformColumns[transfs][tab] is equivalent to TransformColumns[tab,transfs].
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (4)
Transform the difference of columns "a" and "b" into a new column "c":
Double the column "a" and halve the column "b":
Transform existing columns into a new column:
Transform columns on an out-of-core tabular:
Fetch the population and area of the Central American countries, expressed in Tabular form:
Scope (18)
Transformations (7)
Transform an existing column in a Tabular object:
Split an existing column in a Tabular object:
TransformColumns with a function f acts on whole rows as associations if columns are named:
On a Tabular object with anonymous columns, the rows are expressed as lists:
Use the operator form of TransformColumns:
Use "a"Nothing to remove column "a" from the result:
Remove three columns from the result:
Add the second and fourth columns to make a fifth column in a matrix:
With Apply around the function, there is an argument for each column:
Use Key in the Function body of Tabular transformations when the key is a general expression:
Input Data (3)
Transform a list of associations:
Create a new column as a function of existing columns:
Transform a Dataset object:
Columnwise Operations (4)
Use ColumnwiseValue to subtract the mean of a column from its values:
Find which elements in a column are above the median:
Include a constant column with the median value:
Compute the median only once by using the operator form:
Use ColumnwiseThread to compute a vector-valued transformation of entire columns:
With ColumnwiseValue, you get the same list for each row:
Take a Tabular object:
TransformColumns by default operates sequentially on each row:
TransformColumns with ColumnwiseValue[expr] evaluates expr once first, then acts on each row:
TransformColumns with ColumnwiseThread[expr] evaluates expr once, acting on whole columns:
Placement of Columns (2)
Take a Tabular object:
By default, TransformColumns places new columns at the end:
Use column "b" as an anchor column after which the new column is placed:
Place the new column after column "a":
Place the new column before column "a":
Use column names without a transformation to anchor column placement in the result:
By default, new columns are appended on the right:
Place "e" before "a" and "f" after "b":
Place "e" first and "f" after "b" and remove "a" from the result:
Missing Fallback (2)
Use MissingFallback to fill in missing values when transforming a Tabular object:
Use row values from the previous column:
Use row values from the next column:
Use functions of columns in MissingFallback to fill in missing values when transforming a Tabular object:
Applications (3)
Medical Data (1)
This data contains information on kidney transplant patients—time in weeks to death or on-study time since transplant at the given age:
Use TransformColumns to give meaning to the numerically encoded data:
Now use the categories to compute mean survival time in years with PivotTable:
Weather Data (1)
Weather data from JFK airport in C, mbar and km/h:
Create a Tabular object with new column:
Lake Mead Levels (1)
Time series of Lake Mead water levels:
Create a Tabular object:
Split the dates into year and month columns using TransformColumns and remove "Date" column:
Use PivotToColumns to convert into a more compact form for visualization:
Properties & Relations (3)
TransformColumns keeps all the columns not being transformed:
ConstructColumns keeps only the listed columns:
TransformColumns can be used to remove columns:
Equivalently, use DeleteColumns:
Take a Tabular object whose columns are years and months:
TransformColumns can add a new column by constructing a date for each row:
Alternatively, first construct the column of dates and then use InsertColumns to append it:
Text
Wolfram Research (2025), TransformColumns, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TransformColumns.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "TransformColumns." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TransformColumns.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). TransformColumns. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TransformColumns.html