List
Background & Context
-
- Column of numbers or strings.
- Stores a list of numbers or strings as lines.
- Plain text format.
- Is essentially a single-column version of the "Table" format.
Import & Export

- Import["file","List"] imports a text file, returning each line as a string or a number.
- Export["file",list,"List"] writes any list as a column of numbers or strings.
- Import["file","List"] returns a list of strings or numbers, each representing a line of file.
- Export["file",list,"List"] exports list as a column, writing the CForm of each element as a separate line.
- Import["file",{"List",elem} ] imports the specified element from a "List" file.
- Import["file",{"List",elem,suba,subb,…}] imports a subelement.
- Import["file",{"List",{elem1,elem2,…}}] imports multiple elements.
- The format "List" must be explicitly given.
- Export["file",expr, {"List",elem}] creates a "List" file by treating expr as specifying element elem.
- Export["file",{expr1,expr2,…},{"List",{elem1,elem2,…}}] treats each expri as specifying the corresponding elemi.
- Export["file",expr,"List",opt1->val1,…] exports expr with the specified option elements taken to have the specified values.
- Export["file",{elem1->expr1,elem2->expr2,…},{"List","Rules"}] uses rules to specify the elements to be exported.
- See the following reference pages for full general information:
-
Import, Export import from or export to a file CloudImport, CloudExport import from or export to a cloud object ImportString, ExportString import from or export to a string ImportByteArray, ExportByteArray import from or export to a byte array
Import Elements

- General Import elements:
-
"Elements" list of elements and options available in this file "Summary" summary of the file "Rules" list of rules for all available elements - Data representation elements:
-
"Data" list of numbers or strings, each representing a line "Grid" list data as a Grid object - Import and Export use the "Data" element by default.
Options
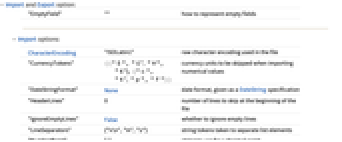

- Import and Export option:
-
"EmptyField" "" how to represent empty fields - Import options:
-
CharacterEncoding "ISOLatin1" raw character encoding used in the file "CurrencyTokens" {{"$", " 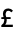 ", "
", "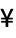 ", "
", "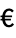 "}, {"c", "
"}, {"c", "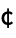 ", "p", "F"}}
", "p", "F"}}currency units to be skipped when importing numerical values "DateStringFormat" None date format, given as a DateString specification "HeaderLines" 0 number of lines to skip at the beginning of the file "IgnoreEmptyLines" False whether to ignore empty lines "LineSeparators" {"∖r\n","∖n","\r"} string tokens taken to separate list elements "NumberPoint" "." string to use for a decimal point "NumberSigns" {"-","+"} strings to use for signs of negative and positive numbers "Numeric" True whether to import data fields as numbers if possible - With CharacterEncoding -> Automatic, Import will attempt to infer the character encoding of the file.
- Import converts table entries formatted as specified by the "DateStringFormat" option to a DateList representation of the form {y,m,d,h,m,s}.
- Empty lines and lines containing only whitespace characters are converted to an empty string by default. With "IgnoreEmptyLines" set to True, Import will skip empty lines.
- With "Numeric"->False, numbers will be imported as strings in the form they appear in the file.
- All common conventions for the encoding of newline characters are recognized with the default setting of "LineSeparators".
- General Export options:
-
Alignment None how data is aligned within table columns CharacterEncoding "UTF8" raw character encoding used in the file - Possible settings for Alignment are None, Left, Center, and Right.
Examples
Basic Examples (4)
Import a text file as a list of strings:
Import converts records to integers or reals if possible:
Currency symbols are automatically omitted when importing as a list:
See Also
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 1999 (4.0) | Updated in 2019 (12.0)