ChineseRemainder[{r1,r2,…},{m1,m2,…}]
gives the smallest ![]() with
with ![]() that satisfies all the integer congruences
that satisfies all the integer congruences ![]() .
.
ChineseRemainder[{r1,r2,…},{m1,m2,…},d]
gives the smallest ![]() with
with ![]() that satisfies all the integer congruences
that satisfies all the integer congruences ![]() .
.


ChineseRemainder
ChineseRemainder[{r1,r2,…},{m1,m2,…}]
gives the smallest ![]() with
with ![]() that satisfies all the integer congruences
that satisfies all the integer congruences ![]() .
.
ChineseRemainder[{r1,r2,…},{m1,m2,…},d]
gives the smallest ![]() with
with ![]() that satisfies all the integer congruences
that satisfies all the integer congruences ![]() .
.
Details
- If no solution for
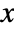 exists, ChineseRemainder returns unevaluated.
exists, ChineseRemainder returns unevaluated. - If all 0≤ri<mi, then the result satisfies
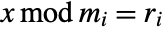 .
. - ChineseRemainder[{r1,r2,…},{m1,m2,…}] gives a solution
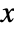 with
with 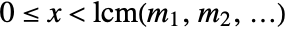 .
. - ChineseRemainder[{r1,r2,…},{m1,m2,…},d] gives a solution
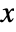 with
with 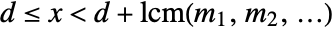 .
.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Applications (3)
Properties & Relations (1)
Solve congruential equations using Reduce or FindInstance:
See Also
Function Repository: IntegerSpectralDecomposition IntegerSpectralBasis
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), ChineseRemainder, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChineseRemainder.html (updated 2016).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "ChineseRemainder." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2016. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChineseRemainder.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). ChineseRemainder. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChineseRemainder.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_chineseremainder, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ChineseRemainder}", year="2016", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChineseRemainder.html}", note=[Accessed: 15-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_chineseremainder, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ChineseRemainder}, year={2016}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ChineseRemainder.html}, note=[Accessed: 15-February-2026]}