



Mod
Details

- Mod is also known as modulo operation.
- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
- Typically used in modular arithmetic, cryptography, random number generation and cyclic operations in programs.
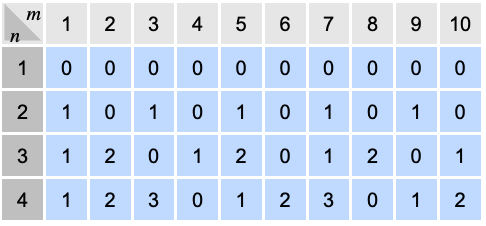
- Mod[m,n] gives the remainder of m divided by n.
- Mod[m,n] is equivalent to m-n Quotient[m,n].
- For positive integers m and n, Mod[m,n] is an integer between 0 and n-1.
- Mod[m,n,d] gives a result
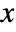 such that
such that 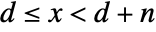 and
and 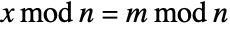 .
.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (13)
Numerical Evaluation (6)
Applications (19)
Basic Applications (3)
Numeric Identifiers (1)
Cryptography (2)
Build an RSA-like encryption scheme. Start with the modulus:
Find the universal exponent of the multiplication group modulo n:
Use Mod to create a Caesar cipher that shifts letters in the alphabet to encrypt a message:
Number Theory (6)
Check if numbers of the form ![]() are prime or composite:
are prime or composite:
Select primes below 100 having the form of ![]() :
:
Define a notation for addition modulo 2:
Use Mod to solve systems of linear congruences:
Computer Sciences (3)
Politics, Economics and Social Sciences (2)
Properties & Relations (7)
Mod is a periodic function:
Mod is defined over all complex numbers:
Mod is transitive. If ![]() and
and ![]() , then
, then ![]() :
:
The QuotientRemainder[a,n] is the same as Mod[a,n]:
Use PowerMod to compute the modular inverse:
The results have the same sign as the modulus:
For a positive real number x, Mod[x,1] gives the fractional part of x:
Possible Issues (1)
Some computations may require higher internal precision than the default:
Reset the value of $MaxExtraPrecision:
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 1996 (3.0) ▪ 1999 (4.0) ▪ 2000 (4.1) ▪ 2002 (4.2)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Mod, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Mod.html (updated 2002).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Mod." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2002. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Mod.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Mod. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Mod.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_mod, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Mod}", year="2002", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Mod.html}", note=[Accessed: 03-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_mod, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Mod}, year={2002}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Mod.html}, note=[Accessed: 03-March-2026]}