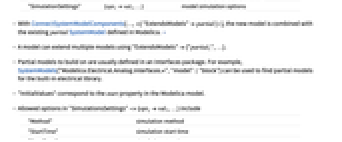
ConnectSystemModelComponents[{"c1"∈comp1,…},{"c1.a""c2.b",…}]
creates a system model by connecting connector "a" of component "c1" with connector "b" of component "c2" etc.


ConnectSystemModelComponents
ConnectSystemModelComponents[{"c1"∈comp1,…},{"c1.a""c2.b",…}]
creates a system model by connecting connector "a" of component "c1" with connector "b" of component "c2" etc.
Details and Options


- ConnectSystemModelComponents assembles components to create a new system model. These connections communicate values and set conservation laws in the system.
- ConnectSystemModelComponents returns SystemModel[…].
- ConnectSystemModelComponents["NewModel",…] gives the created model the name "NewModel".
- ConnectSystemModelComponents["PackageA.NewModel",…] inserts "NewModel" into "PackageA".
- The compi can be a SystemModel object, a full model name string or a shortened model name accepted by SystemModel.
- In ConnectSystemModelComponents[…,spec], spec is an Association with the following keys:
-
"ParameterValues" {p1val1,…} parameter values "InitialValues" {v1val1,…} initial values "ExtendsModels" {partial1,…} partial models to build on "DiscreteVariables" {v1,v2,…} variables changing only at events "SimulationSettings" {opt1val1,…} model simulation options - With ConnectSystemModelComponents[…,"ExtendsModels"partial], the new model is combined with the existing partial SystemModel defined in Modelica. »
- A model can extend multiple models using "ExtendsModels"{"partial1",…}.
- Partial models to build on are usually defined in an Interfaces package. For example, SystemModels["Modelica.Electrical.Analog.Interfaces.*","model"|"block"] can be used to find partial models for the built-in electrical library.
- "InitialValues" correspond to the start property in the Modelica model.
- Allowed options in "SimulationsSettings"->{opt1val1,…} include
-
"Method" simulation method "StartTime" simulation start time "StopTime" simulation stop time - Available adaptive-step "Method" values include:
-
"DASSL" DASSL DAE solver "CVODES" CVODES ODE solver - Options for adaptive-step methods include:
-
"InterpolationPoints" number of interpolation points "Tolerance" tolerance for adaptive step size - Available fixed-step "Method" values include:
-
"Euler" explicit Euler's method of order 1 "Heun" Heun's method of order 2 "RungeKutta" explicit Runge–Kutta method of order 4 - Options for fixed-step methods include:
-
"StepSize" fixed step size - The layout for the created model diagram can be controlled with the option GraphLayout.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (5)
Create a block example, sampling a sine wave at regular intervals:
Simulate and plot the sampled signal:
Give a value to a parameter in a component:
Set the amplitude of the sine to 3:
Connect two masses with heat capacity with a thermal conductor:
Set heat capacities, masses and initial temperatures:
Show that a temperature equilibrium is reached:
Create a mass connected to a spring:
Move the initial position of the mass, stretching the spring:
Generalizations & Extensions (1)
Rule, DirectedEdge and UndirectedEdge can be used for connections:
Use Rule to specify a connection:
Use DirectedEdge and UndirectedEdge to specify connections:
Options (3)
GraphLayout (3)
GraphLayout can be used to specify the layout of the model diagram:
An edge-weighted "SpringElectricalEmbedding" is used by default:
Applications (3)
A DC Motor (1)
A Lowpass Filter (1)
An Inerter (1)
Create an inerter, with forces at the terminals proportional to relative acceleration:
Compare how adding an inerter to a damping system influences vibrations:
Set parameter values and simulate the system with a sine vibration force:
Damping effects are of similar magnitude:
Forces acting on the damper component are significantly reduced with an inerter:
Properties & Relations (3)
Use CreateSystemModel to create models based on differential equations:
CreateSystemModel can be used similarly to ConnectSystemModelComponents:
Hierarchical models based on existing components enable quick creation of larger systems:
Build a 3D inverted pendulum model with a controller:
A complex multidomain system can be built using few components:
See Also
Related Guides
Related Links
Text
Wolfram Research (2018), ConnectSystemModelComponents, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ConnectSystemModelComponents.html (updated 2020).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2018. "ConnectSystemModelComponents." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2020. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ConnectSystemModelComponents.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2018). ConnectSystemModelComponents. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ConnectSystemModelComponents.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_connectsystemmodelcomponents, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ConnectSystemModelComponents}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ConnectSystemModelComponents.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_connectsystemmodelcomponents, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ConnectSystemModelComponents}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ConnectSystemModelComponents.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}