CreateSemanticSearchIndex[source]
creates a search index from the data in source.
CreateSemanticSearchIndex[{source1,…}]
creates a search index with a collection of sources sourcei.
CreateSemanticSearchIndex[{source1val1,…}]
associates the source sourcei to the value vali.
CreateSemanticSearchIndex[data,"name"]
gives the search index the specified name.


CreateSemanticSearchIndex
CreateSemanticSearchIndex[source]
creates a search index from the data in source.
CreateSemanticSearchIndex[{source1,…}]
creates a search index with a collection of sources sourcei.
CreateSemanticSearchIndex[{source1val1,…}]
associates the source sourcei to the value vali.
CreateSemanticSearchIndex[data,"name"]
gives the search index the specified name.
Details and Options


- CreateSemanticSearchIndex is used to extract features from text that can be used to search the content semantically.
- Possible values for source are:
-
"string" a plain string File["path"] individual file URL["url"] the text representation of "url" CloudObject[…] a cloud object LocalObject[…] a local object ContentObject[…] a content object {source1,source2,…} list of sources - Sources can be annotated. Every chunk from a given source will have the same annotation.
- Possible ways to specify annotations include:
-
{source1val1,…} a list of sources and associated values {source1,…}{val1,…} a rule between sources and values - Accepted forms of vali include:
-
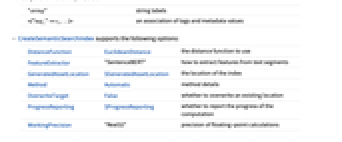
"string" string labels <|"tag1"v1,…|> an association of tags and metadata values - CreateSemanticSearchIndex supports the following options:
-
DistanceFunction EuclideanDistance the distance function to use FeatureExtractor "MiniLM" how to extract features from text chunks GeneratedAssetLocation $GeneratedAssetLocation the location of the index Method Automatic method details OverwriteTarget Automatic whether to overwrite an existing location ProgressReporting $ProgressReporting whether to report the progress of the computation WorkingPrecision "Real32" precision of floating-point calculations - Possible values for DistanceFunction include EuclideanDistance, SquaredEuclideanDistance, CosineDistance, JaccardDissimilarity and HammingDistance.
- Possible values for FeatureExtractor include:
-
"SentenceBERT" a local model based on SentenceBERT LLMConfiguration an LLM-based sentence embedding f a custom extractor function - Custom extractors f must operate on a list of strings and produce a list of vectors of the same length.
- Detailed options can be given using Method<|opt1val1|>. Possible values for opti are:
-
"ContextPadding" 
minimal overlap between chunks "MaximumItemLength" 
maximum length of a text chunk "MinimumItemLength" 
minimum length of a text chunk "SplitPattern" Automatic where to split long strings - The automatic "SplitPattern" tries to split a source text in paragraphs, newlines and words to create chunks between "MinimumItemLength" and "MaximumItemLength".
- Possible settings for WorkingPrecision include:
-
"Integer8" signed 8-bit integers from -128 through 127 "Real32" single-precision real (32-bit) "Real64" double-precision real (64-bit)
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Create a new SemanticSearchIndex:
Search in the text by semantic similarity:
Scope (6)
Data Sources (4)
Annotations (2)
Annotate sources with a label:
Each chunk inherits the correspondent source label:
The label is returned when performing search:
Annotated sources with tagged metadata:
Specify the annotations in a separate Association:
Options (10)
DistanceFunction (1)
Specify a custom distance function for the index:
By default, EuclideanDistance is used:
FeatureExtractor (1)
GeneratedAssetLocation (3)
Method (2)
Create a text with multiple very short entries:
The entire text will be embedded as a single chunk:
Adjusting the minimum and maximum item length to chunk into more relevant sections:
Create several paragraphs of text:
Join them with nonstandard separators:
The default automatic paragraph and sentence chunking will give poor results:
Use a custom split pattern to create chunks at the custom dividers:
OverwriteTarget (2)
The index's automatic location is determined by its name:
With default OverwriteTargetAutomatic, a new index name is generated to avoid collisions:
To force overwriting, use OverwriteTargetTrue:
Use OverwriteTargetFalse to perform a strict check:
OverwriteTargetFalse will also prevent reusing the same index name in a different location:
By default, existing files are not overwritten:
Use OverwriteTargetTrue to overwrite the existing file:
Applications (2)
Properties & Relations (1)
Create an index and retrieve the embeddings:
FeatureExtract can use the specified "SentenceVector" extractor to create similar embeddings:
Possible Issues (2)
An input string is always interpreted as text:
To follow the link, use the URL wrapper:
Use File to import file content:
Text with multiple small entries:
Chunking will not occur, as the length of the string is less than the default maximum:
Lower the maximum item length to ensure chunking takes place:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2024), CreateSemanticSearchIndex, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CreateSemanticSearchIndex.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2024. "CreateSemanticSearchIndex." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CreateSemanticSearchIndex.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2024). CreateSemanticSearchIndex. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CreateSemanticSearchIndex.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_createsemanticsearchindex, author="Wolfram Research", title="{CreateSemanticSearchIndex}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CreateSemanticSearchIndex.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_createsemanticsearchindex, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={CreateSemanticSearchIndex}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CreateSemanticSearchIndex.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}