KaiserWindow[x]
represents a Kaiser window function of x.
KaiserWindow[x,α]
uses the parameter α.


KaiserWindow
KaiserWindow[x]
represents a Kaiser window function of x.
KaiserWindow[x,α]
uses the parameter α.
Details

- KaiserWindow, also know as Kaiser–Bessel window, is a window function typically used for finite impulse response (FIR) filter design and spectral analysis.
- Window functions are used in applications where data is processed in short segments and have a smoothing effect by gradually tapering data values to zero at the ends of each segment.
- KaiserWindow[x,α] is equivalent to
 for -
for -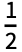 ≤x≤
≤x≤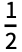 and 0 otherwise.
and 0 otherwise. - KaiserWindow[x] is equivalent to KaiserWindow[x,3].
- KaiserWindow automatically threads over lists.
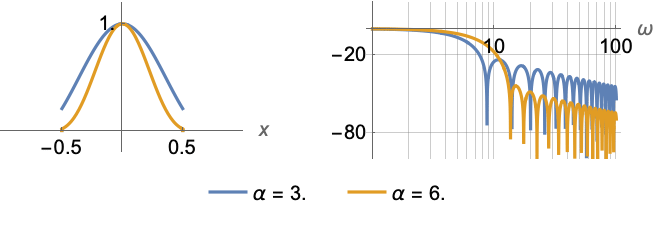
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (8)
Applications (5)
Use the Kaiser window to diminish the effect of signal partitioning when computing the spectrogram:
Create a lowpass FIR filter with cutoff frequency of ![]() and length 15:
and length 15:
Apply a Kaiser window to the filter to improve stopband attenuation:
Log-magnitude plot of the power spectra of the two filters:
Filter a white noise signal using the Kaiser window method:
Use a window specification to calculate sample PowerSpectralDensity of an ARMA process:
Compare to spectral density calculated without a windowing function:
The plot shows that window smooths the spectral density:
Compare to the theoretical spectral density of the process:
Properties & Relations (8)
The area under the Kaiser window:
Normalize to create a window with unit area:
Fourier transform of the Kaiser window:
Power spectrum of the Kaiser window:
Fourier transform of the parametrized Kaiser window:
Variation of the magnitude spectrum as a function of the parameter α:
Discrete Kaiser window of length 15:
Normalize so the coefficients add up to 1:
Discrete-time Fourier transform of a normalized discrete Kaiser window of length 15:
Power spectra of the default Kaiser and rectangular windows:
Power spectra for three different window lengths:
Power spectra for three different values of the shape parameter α:
Possible Issues (1)
Two-dimensional sampling of Kaiser window will use a different parameter for each row of samples when passed as a symbol to Array:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), KaiserWindow, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/KaiserWindow.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "KaiserWindow." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/KaiserWindow.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). KaiserWindow. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/KaiserWindow.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_kaiserwindow, author="Wolfram Research", title="{KaiserWindow}", year="2012", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/KaiserWindow.html}", note=[Accessed: 01-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_kaiserwindow, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={KaiserWindow}, year={2012}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/KaiserWindow.html}, note=[Accessed: 01-March-2026]}