MagneticPotentialCondition[pred,vars,pars]
represents a magnetic surface potential boundary condition for PDEs with predicate pred indicating where it applies, with model variables vars and global parameters pars.
MagneticPotentialCondition[pred,vars,pars,lkey]
represents a magnetic potential surface boundary condition with local parameters specified in pars[lkey].


MagneticPotentialCondition
MagneticPotentialCondition[pred,vars,pars]
represents a magnetic surface potential boundary condition for PDEs with predicate pred indicating where it applies, with model variables vars and global parameters pars.
MagneticPotentialCondition[pred,vars,pars,lkey]
represents a magnetic potential surface boundary condition with local parameters specified in pars[lkey].
Details

- MagneticPotentialCondition specifies a Dirichlet boundary condition for MagnetostaticPDEComponent and MagneticPDEComponent.
- MagneticPotentialCondition is typically used to set a specific magnetic potential on the boundary.
- MagneticPotentialCondition sets a scalar magnetic potential on the boundary with dependent variable
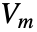 and independent variables
and independent variables 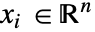 .
. - Stationary variables vars are vars={Vm[x1,…,xn],{x1,…,xn}}.
- MagneticPotentialCondition sets a vector magnetic potential on the boundary with dependent variable
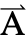 and independent variables
and independent variables 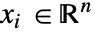 .
. - The vector-valued dependent variable
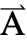 is specified as a three-vector
is specified as a three-vector 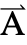 ={Ax1,Ax2,Ax3}.
={Ax1,Ax2,Ax3}. - Stationary variables vars are vars={
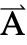 [x1,…,xn],{x1,…,xn}}.
[x1,…,xn],{x1,…,xn}}. - Frequency-dependent variables vars are vars={
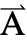 [x1,…,xn],ω,{,…,xn}}.
[x1,…,xn],ω,{,…,xn}}. - Time-dependent variables vars are vars={
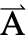 [t,x1,…,xn],t,{x1,…,xn}}.
[t,x1,…,xn],t,{x1,…,xn}}. - The following additional model parameters pars can be given:
-
parameter default symbol "MagneticPotential" - 0
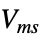 , magnetic surface potential in [
, magnetic surface potential in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "A", amperes, "Amperes"}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "A", amperes, "Amperes"}, QuantityTF]](Files/MagneticPotentialCondition.en/11.png) ]
]"MagneticPotential" - {0,…}
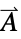 , magnetic surface potential in [
, magnetic surface potential in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"A", , "/", , {"m", ^, 2}}, amperes per meter squared, {{(, "Amperes", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 2}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"A", , "/", , {"m", ^, 2}}, amperes per meter squared, {{(, "Amperes", )}, /, {(, {"Meters", ^, 2}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/MagneticPotentialCondition.en/13.png) ]
] - Model parameters pars are specified as for MagnetostaticPDEComponent or MagneticPDEComponent.
- MagneticPotentialCondition evaluates to one or more DirichletCondition instances.
- The boundary predicate pred can be specified as in DirichletCondition.
- If the MagneticPotentialCondition depends on parameters
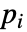 that are specified in the association pars as …,keypi…,pivi,…, the parameters
that are specified in the association pars as …,keypi…,pivi,…, the parameters 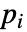 are replaced with
are replaced with 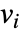 .
.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (2)
Applications (3)
To model a permanent magnet in 2D with a rectangular cross section, define the mesh to use:
Visualize the internal boundaries of the magnet region:
Define the magnetostatic operator:
Define the zero magnetic scalar potential condition at the exterior boundaries:
Solve the magnetostatic PDE model:
Visualize the magnetic scalar potential and the magnetic field:
To model a 3D cylinder permanent magnet, set up variables:
Define the magnet region of height ![]() [
[![]() ] and radius
] and radius ![]() [
[![]() ]:
]:
Define the magnetization vector:
Set up the mesh with a sphere of air of ![]() [
[![]() ] that represents the surrounding volume:
] that represents the surrounding volume:
Visualize the magnet cylinder that is inside the mesh:
Set up the magnetostatIc PDE component:
Define the mesh to model a long copper wire of circular cross section:
Define the parameters of the model:
Define the uniform external current density in the ![]() direction:
direction:
Define a zero magnetic potential condition at the exterior boundary:
Set up an angular frequency of 800 Hz:
Replace the angular frequency ![]() of the equation with the frequency and solve the PDE:
of the equation with the frequency and solve the PDE:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2025), MagneticPotentialCondition, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MagneticPotentialCondition.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "MagneticPotentialCondition." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MagneticPotentialCondition.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). MagneticPotentialCondition. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MagneticPotentialCondition.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_magneticpotentialcondition, author="Wolfram Research", title="{MagneticPotentialCondition}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MagneticPotentialCondition.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_magneticpotentialcondition, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={MagneticPotentialCondition}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MagneticPotentialCondition.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}