PaddingLayer[{{m1,n1},{m2,n2},…}]
represents a net layer that pads an input array with mi elements at the beginning and ni elements at the end at level i of the array.


PaddingLayer
PaddingLayer[{{m1,n1},{m2,n2},…}]
represents a net layer that pads an input array with mi elements at the beginning and ni elements at the end at level i of the array.
Details and Options
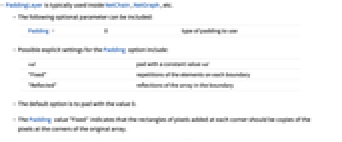

- PaddingLayer is typically used inside NetChain, NetGraph, etc.
- The following optional parameter can be included:
-
Padding 0 type of padding to use - Possible explicit settings for the Padding option include:
-
val pad with a constant value val "Fixed" repetitions of the elements on each boundary "Reflected" reflections of the array in the boundary - The default option is to pad with the value 0.
- The Padding value "Fixed" indicates that the rectangles of pixels added at each corner should be copies of the pixels at the corners of the original array.
- PaddingLayer exposes the following ports for use in NetGraph etc.:
-
"Input" an array of rank 1 or higher "Output" an array of rank 1 or higher - When it cannot be inferred from other layers in a larger net, the option "Input"{d1,…,dn} can be used to fix the input of PaddingLayer to be an array of dimensions d1×…×dn.
- PaddingLayer[…][input] explicitly computes the output from applying the layer.
- PaddingLayer[…][{input1,input2,…}] explicitly computes outputs for each of the inputi.
- When given a NumericArray as input, the output will be a NumericArray.
- Options[PaddingLayer] gives the list of default options to construct the layer. Options[PaddingLayer[…]] gives the list of default options to evaluate the layer on some data.
- Information[PaddingLayer[…]] gives a report about the layer.
- Information[PaddingLayer[…],prop] gives the value of the property prop of PaddingLayer[…]. Possible properties are the same as for NetGraph.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Create a PaddingLayer that pads a vector with zeros:
Create a PaddingLayer that pads a vector with zeros:
Scope (3)
Arguments (2)
Create a PaddingLayer that pads a vector with zeros:
The layer threads across a batch of examples:
Create a PaddingLayer that pads a matrix:
Ports (1)
Create a PaddingLayer that pads an image encoded as a 3-dimensional array, using "Fixed" padding:
Options (3)
Properties & Relations (1)
PaddingLayer is equivalent to ArrayPad:
PaddingLayer also supports the "Fixed" padding type:
See Also
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2017), PaddingLayer, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PaddingLayer.html (updated 2017).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2017. "PaddingLayer." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2017. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PaddingLayer.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2017). PaddingLayer. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PaddingLayer.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_paddinglayer, author="Wolfram Research", title="{PaddingLayer}", year="2017", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PaddingLayer.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_paddinglayer, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={PaddingLayer}, year={2017}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PaddingLayer.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}