lhs=rhs
evaluates rhs and assigns the result to be the value of lhs. From then on, lhs is replaced by rhs whenever it appears.
{l1,l2,…}={r1,r2,…}
evaluates the ri, and assigns the results to be the values of the corresponding li.


Set 
lhs=rhs
evaluates rhs and assigns the result to be the value of lhs. From then on, lhs is replaced by rhs whenever it appears.
{l1,l2,…}={r1,r2,…}
evaluates the ri, and assigns the results to be the values of the corresponding li.
Details
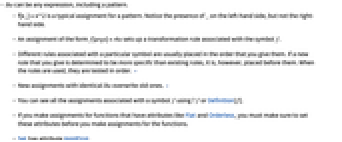
- lhs can be any expression, including a pattern.
- f[x_]=x^2 is a typical assignment for a pattern. Notice the presence of _ on the left‐hand side, but not the right‐hand side.
- An assignment of the form f[args]=rhs sets up a transformation rule associated with the symbol f.
- Different rules associated with a particular symbol are usually placed in the order that you give them. If a new rule that you give is determined to be more specific than existing rules, it is, however, placed before them. When the rules are used, they are tested in order. »
- New assignments with identical lhs overwrite old ones. »
- You can see all the assignments associated with a symbol f using ?f or Definition[f].
- If you make assignments for functions that have attributes like Flat and Orderless, you must make sure to set these attributes before you make assignments for the functions.
- Set has attribute HoldFirst.
- If lhs is of the form f[args], then args are evaluated. »
- There are some special functions for which an assignment to s[f[args]] is automatically associated with f rather than s. These functions include: Attributes, Default, Format, MessageName, Messages, N, and Options. »
- When it appears in an unevaluated symbolic form, Set is treated as a scoping construct so that variables in nested occurrences are renamed if necessary. »
- lhs=rhs returns rhs even if for some reason the assignment specified cannot be performed.
- Some global variables such as $RecursionLimit can only be assigned a certain range or class of values.
Background & Context
- Set is a function that evaluates and assigns an expression to be the value of a variable. The expression
![Set[lhs,rhs] Set[lhs,rhs]](Files/Set.en/1.png) is commonly represented using the shorthand syntax
is commonly represented using the shorthand syntax 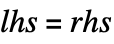 . After Set is evaluated, lhs is replaced by rhs whenever it appears. Depending on the form of lhs, the result is stored as in the associated OwnValues, DownValues, or a specialized data structure.
. After Set is evaluated, lhs is replaced by rhs whenever it appears. Depending on the form of lhs, the result is stored as in the associated OwnValues, DownValues, or a specialized data structure. - Set often contains patterns on the lhs that are assigned transformed values as indicated on the rhs, e.g.
![f[x_] = x^2 f[x_] = x^2](Files/Set.en/3.png) .
. 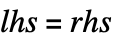 evaluates rhs immediately, so in situations where rhs should be evaluated only after the assignment is made, SetDelayed (written in shorthand as :=) should be used instead.
evaluates rhs immediately, so in situations where rhs should be evaluated only after the assignment is made, SetDelayed (written in shorthand as :=) should be used instead. - The assignments associated with a given symbol can be seen using Definition[f]. Individual assignments may be removed from a symbol using Unset; Clear and ClearAll remove all definitions at once.
Examples
open all close allScope (15)
Left-Hand Sides (7)
Set values for "indexed variables":
Define a function from an expression:
Use Block to temporarily set variables:
Different Kinds of Values (8)
A definition for Attributes is associated with ![]() , rather than Attributes:
, rather than Attributes:
Generalizations & Extensions (5)
Applications (6)
Compute the GCD of two numbers:
Compute ![]() using Newton's method:
using Newton's method:
Use a variable as an abbreviation for a complicated expression used more than once:
A scalar implementation of backsubstitution in a system of linear equations:
A vector implementation of backsubstitution in a system of linear equations:
Properties & Relations (9)
The right side of an immediate definition is evaluated when the definition is made:
The right side of a delayed definition is evaluated each time the definition is used:
The arguments of the left side of a definition are evaluated before the definition is made:
Definitions with the same left side overwrite earlier ones:
Make definitions for special and general cases using immediate and delayed assignments:
More specific definitions are put in front of more general ones:
The pattern variable is renamed if necessary inside a nested scope:
Module introduces new symbols, distinct from global ones:
Definition prints definitions associated with a symbol:
Information prints various information about a symbol, including any definitions:
OwnValues returns a list of rules corresponding to any downvalues defined:
Use Unset (=.) to clear definitions with a particular left-hand side:
Possible Issues (4)
Neat Examples (1)
Compute the arithmetic-geometric mean of two numbers [more info]:
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Set, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Set.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Set." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Set.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Set. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Set.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_set, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Set}", year="1988", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Set.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_set, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Set}, year={1988}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Set.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}