TreeExtract[tree,pos]
extracts the subtree of tree at the position specified by pos.
TreeExtract[tree,{pos1,pos2,…}]
extracts a list of subtrees of tree.
TreeExtract[tree,pos,h]
extracts subtrees of tree, applying h to each subtree.
TreeExtract[pos]
represents an operator form of TreeExtract that can be applied to a tree.


TreeExtract
TreeExtract[tree,pos]
extracts the subtree of tree at the position specified by pos.
TreeExtract[tree,{pos1,pos2,…}]
extracts a list of subtrees of tree.
TreeExtract[tree,pos,h]
extracts subtrees of tree, applying h to each subtree.
TreeExtract[pos]
represents an operator form of TreeExtract that can be applied to a tree.
Details

- TreeExtract allows extraction of properties of subtrees at any position in a Tree object.
- For integers i, j, …, TreeExtract[tree,{i,j,…}] extracts the subtree at position {i,j,…}. »
- TreeExtract can use the position specifications returned by TreePosition as well as extended forms as used in functions such as TreeInsert and TreeReplacePart. »
- An individual position specification pos can be given as {part1,part2,…}, where part specifications parti include:
-
i the i 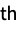 child
child-i the i 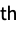 child from the end
child from the end{i1,i2,…} the list of children with part numbers i1, i2, … All all children m;;n children m through n "key" the child whose key is "key" Key[k] the child with an arbitrary key k TreeLevel[levelspec] the subtrees on levels specified by levelspec TreeCases[pattern] the subtrees with data matching pattern TreeSelect[crit] the subtrees for which crit gives True - In TreeExtract[tree,{p1,p2,…}], {p1,p2,…} is interpreted as a list of individual position specifications if all the pi are lists. Otherwise, {p1,p2,…} will be taken to be an individual position specification. »
- Specifications that extract multiple parts at one level retain the data at that level. »
- TreeExtract works on trees containing an Association of subtrees, using the same specification for keys as in Part. »
- TreeExtract[pos][tree] is equivalent to TreeExtract[tree,pos].
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Extract the second child of a tree:
Extract a subtree at any position:
Extract a list of subtrees at several positions:
Perform independent extractions at consecutive levels:
Use the operator form of TreeExtract:
Scope (23)
Part Specifications (9)
Single versus Multiple Positions (3)
Forms Involving All (2)
Extract the children of the second child:
Extract the second child of each child:
Extract the first and third child of each child:
Extract the first and third child of each child separately:
Extracting using All preserves the data at that level:
Associations (5)
Extract a subtree from a tree containing an association by key:
If the key is a string, the Key wrapper is optional:
Extract a subtree from a tree containing an association by key:
Extract a subtree from a tree containing an association by position:
Extract several subtrees from a tree containing an association:
Extract a nested subtree from a tree containing an association:
Extract several nested subtrees from a tree containing an association:
Spans and Sublists (4)
Extract the third through fifth children of a list:
Extract the children at odd positions:
Extract the first three children from each child:
Extract the first and last child from each child:
Extract the first child of the second through fourth children:
Extract the second child of the first, third and fourth children:
Extract the first, second and fifth children of the last three children:
Properties & Relations (10)
Construct a tree from the heads in an expression:
TreeExtract extracts a subtree of a tree:
This corresponds to extracting a subexpression of an expression:
Extract can extract subexpressions directly:
If pos is not a list, pos and {pos} are equivalent specifications:
For a list of integers {i,j,…}, TreeExtract[tree,{i,j,…}] is equivalent to …@TreeExtract[j]@TreeExtract[i]@tree:
TreeExtract[tree,{{i1,j1,…},{i2,j2,…},…}] is equivalent to {TreeExtract[tree,{i1,j1,…}],TreeExtract[tree,{i2,j2,…}],…}:
This extends to the empty list:
Extracting position {} extracts the whole tree:
TreeExtract extracts subtrees repeatedly if a position is mentioned repeatedly:
TreeExtract can use the lists of positions returned by TreePosition:
In TreeExtract[tree,{pos1,pos2,…},h], h wraps the result of extracting the subtrees at each of the posi:
In TreeExtract[tree,pos,h], h wraps the result of extracting the subtree at position pos:
Specifications that extract multiple parts at one level retain the data at that level:
TreeExtract[tree,{p1,p2,…}] treats {p1,p2,…} as a list of individual position specifications if all the pi are lists:
For {{1,2},{3,4}}, the subtrees at positions {1,2} and {3,4} are extracted:
If any pi is not a list, {p1,p2,…} is treated as a list of part specifications:
For {{{1,2},{3,4}}}, parts 3 and 4 of parts 1 and 2 are extracted:
Possible Issues (2)
TreeExtract[tree,{}] returns an empty list of subtrees because the list of positions is empty:
TreeExtract[tree,{{}}] extracts the subtree at position {}, which is the whole tree:
A list of lists in the second argument is always interpreted as a list of position specifications:
As a result, specifications that are equivalent in Part may be treated differently by TreeExtract:
Use a list of lists and remove the extra list at the end if consistency between Part and TreeExtract is needed:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2021), TreeExtract, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreeExtract.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2021. "TreeExtract." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreeExtract.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2021). TreeExtract. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreeExtract.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_treeextract, author="Wolfram Research", title="{TreeExtract}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreeExtract.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_treeextract, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={TreeExtract}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TreeExtract.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}