TuringMachine[rule,init,t]
generates a list representing the evolution of the Turing machine with the specified rule from initial condition init for t steps.
TuringMachine[rule,init]
gives the result of evolving init for one step.
TuringMachine[rule]
is an operator form of TuringMachine that corresponds to one step of evolution.


TuringMachine
TuringMachine[rule,init,t]
generates a list representing the evolution of the Turing machine with the specified rule from initial condition init for t steps.
TuringMachine[rule,init]
gives the result of evolving init for one step.
TuringMachine[rule]
is an operator form of TuringMachine that corresponds to one step of evolution.
Details



- For a 1D Turing machine, each step in the evolution generated by TuringMachine is given in the form {{s,x,dx},{a1,a2,…}}, where the head is in state s, the cells on the tape have values ai, the head is at position x relative to the ai, and has moved dx relative to its starting position.
- If dx is omitted in the initial condition for a Turing machine, it is taken to be 0.
- For a d-dimensional Turing machine, the tape is specified as a d-dimensional array, and the position x and relative position dx are length-d lists.
- The rule for a Turing machine can be given as a list of replacements of the form {si,ai}->{spi,api,offi}, with elements as follows:
-
si state of the head ai value of cell under the head spi new state of the head api new value of cell under the head offi offset by which the head moves - The states and cell values can be integers, patterns, or any other expressions. Individual cell values cannot be lists.
- In one dimension, each offset offi is a single integer; in higher dimensions a list of integers.
- When the states and cell values are taken to be integers in the range 1 to
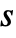 and 0 to
and 0 to 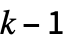 respectively, the following alternative forms can be given for rule:
respectively, the following alternative forms can be given for rule: -
n 2‐state, 2‐color machine with number n {n,s} s‐state, 2‐color machine with number n {n,s,k} s‐state, k‐color machine with number n {n,s,k,r} allow offi in the range 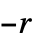 to
to 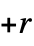 (excluding 0)
(excluding 0) {n,s,k,{r1,r2,…,rd}} 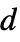 ‐dimensional machine with
‐dimensional machine with 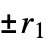 ,
, 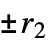 , … offsets
, … offsets{n,s,k,{{off1},{off2},…}} machine allowing the specified explicit offsets {rule,s,k} machine with explicit rule given rule machine with explicit rule given (and s, k inferred) - The number of possible Turing machine rules is as follows:
-
2-state, 2-color machines 4096 s-state, k-color machines (2 s k)^(s k) s-state, k-color, range-r machines (2 r s k)^(s k) 2D s-state, k-color machines (8 s k)^(s k) - If the machine has no rule for the configuration it is in, its configuration will not be changed.
- If a rule has multiple specifications for a given configuration, TuringMachine will use the first one listed.
- The form {rule,s,k} can be used to specify multiway, non-deterministic and other Turing machines in which there is not necessarily exactly one case in the rule for a given configuration.
- Typical forms for the initial conditions init are as follows:
-
{s,{{},0}} head in state s, on a 1D tape filled with 0s {s,{{a1,a2,…},0}} bounded region of values ai on an infinite tape {{s,x},{{a1,a2,…},0}} bounded region with the head initially at position x {{s,…},{{a1,…},{b1,…}}} repetitive background of value bi {{s,…},{a1,a2,…}} finite tape, assumed cyclic - TuringMachine[rule,init,t] generates an evolution list of length
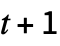 .
. - TuringMachine[rule][init] is equivalent to TuringMachine[rule,init].
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
2-state, 2-color machine 2506 with an initial tape of four 0s, evolving for 3 steps:
2-state, 2-color machine 2506 with an infinite tape of 0s, evolving for 4 steps:
Plot the successive configurations of the tape:
Show the rule icon for a Turing machine:
Plot the evolution, including the state of the head:
Show the rule icon for a Turing machine specified by explicit transitions:
Plot the evolution, including the state of the head:
A Turing machine specified by pattern-based transition rules:
Scope (17)
One-Dimensional Rules (6)
2-state, 2-color machine 2506:
Plot the evolution, including the state of the head:
3-state, 2-color machine 2139050:
2-state, 2-color machine 16220, with range 2:
3-state, 2-color machine 2139050, with jump offsets ![]() and 2:
and 2:
Give explicit transition rules:
Explicitly specify values of the number of states s and the number of colors k for the same transition rules:
Initial Conditions (9)
Head Specification (4)
Tape Specification (5)
Start with a finite tape of four 0s, assumed cyclic:
The left neighbor of the leftmost cell is the rightmost cell, and vice versa:
Start with an infinite tape of 0s:
Start with a tape of 1 on an infinite background of 0s:
Start with a tape consisting of the block 211 on a background of 0s:
Start with the block 211 on a background of repeated 02 blocks:
Applications (12)
Evolution of Wolfram's simplest universal Turing machine from an infinite tape of 0s:
Alternative form using explicit rules:
Show the evolutions of a sequence of 2-state, 2-color machines:
Trajectory of the machine head from successive initial conditions:
Path traced by the head of a 2D machine:
Averaging tape of a 2D machine over many steps:
Successive states sequences from successive initial conditions:
Sequence of left or right movements for successive initial conditions:
Computed function on a one-sided tape:
Show only steps on which the head reaches a new cell:
Show only steps on which the head returns to its initial location:
Properties & Relations (4)
For rules of the form {n,s,k,…}, head states and cell values can be integers in the range 1 to s and 0 to k-1, respectively:
For rules of the form {n,s,k,…}, if the head reaches a cell whose value is not in the range 0 to k-1, the evolution of the machine halts:
Another Turing machine whose evolution halts:
Use an explicit set of rules to define a halting state:
Generate a Turing machine evolution:
"Inject" the state information into a representation of the tape:
Show the position of the head as a red square:
Use RulePlot to generate a complete evolution picture:
Related Guides
Related Links
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), TuringMachine, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TuringMachine.html (updated 2021).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "TuringMachine." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2021. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TuringMachine.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). TuringMachine. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TuringMachine.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_turingmachine, author="Wolfram Research", title="{TuringMachine}", year="2021", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TuringMachine.html}", note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_turingmachine, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={TuringMachine}, year={2021}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TuringMachine.html}, note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}