"Serial" (RS-232 / RS-422 serial protocol)
Device Discovery
Opening the Device
-
The following options can be given:
-
"BaudRate" 9600 data transfer rate in bits per second "DataBits" 8 number of data bits to use per frame "Handshake" None the flow control handshake protocol "IgnoreBreak" False whether to ignore breaks "Parity" None setting for the parity bit "ReadBufferSize" 4096 size of the read buffer in bytes "StopBits" None number of stop bits to use -
Typical baud rate values include: 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, 230400.
-
"DataBits" gives the number of bits in each byte used to carry data. Possible values are: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
-
Possible values for "Parity", specifying how the parity bit should be set, are: None, "Even", "Odd", "Mark", "Space".
-
"StopBits" gives the number of bits used to separate data frames. Possible values are: None, 1, 1.5, 2.
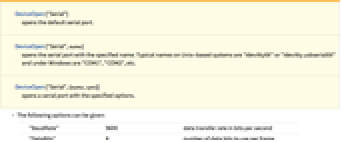
DeviceOpen["Serial"]
opens the default serial port.
DeviceOpen["Serial",name]
opens the serial port with the specified name. Typical names on Unix-based systems are "/dev/ttyXX" or "/dev/tty.usbserialXX" and under Windows are "COM1", "COM2", etc.
DeviceOpen["Serial",{name,opts}]
opens a serial port with the specified options.
Configuring the Device
-
Configuration is not required. Use DeviceOpen to set parameters for the serial connection.
Reading Data

-
Wolfram Language functions such as DeviceReadLatest and DeviceReadTimeSeries are also supported.
-
Bytes are represented in the Wolfram Language by their integer values.
-
Lists of bytes can be converted to character strings using FromCharacterCode.
-
The setting for "ReadTerminator" can be a single byte or character.
-
If no data is available to be read, the read functions will time out after a preset time of 10 seconds.
DeviceRead[dev]
reads a single byte from the serial connection, returning an integer value.
DeviceRead[dev,"String"]
reads a single character from the serial connection, returning the character as a string.
DeviceReadBuffer[dev]
reads all available bytes in the serial connection buffer, returning a list of integers.
DeviceReadBuffer[dev,n]
reads the most recent n bytes in the serial connection buffer.
DeviceReadBuffer[dev,"ReadTerminator"->term]
reads bytes from the serial port buffer until a terminator term.
Writing Data
-
Wolfram Language functions such as DeviceWriteBuffer are also supported.
-
Bytes can be specified either as integers between 0 and 255 or as single-character ASCII strings.
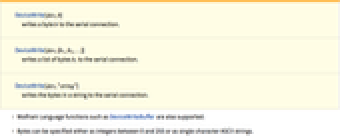
DeviceWrite[dev,b]
writes a byte b to the serial connection.
DeviceWrite[dev,{b1,b2,…}]
writes a list of bytes bi to the serial connection.
DeviceWrite[dev,"string"]
writes the bytes in a string to the serial connection.
Executing Commands
-
The "SerialReadyQ" command can be used to check whether reading from the serial connection could block.
DeviceExecute[dev,"ReadFlush"]
flushes any data that has been read and buffered.
DeviceExecute[dev,"SerialReadyQ"]
gives True if there is any buffered data available for reading, and False otherwise.
Closing and Releasing Resources
DeviceClose[dev]
closes the serial connection and frees related resources.
Examples
Basic Examples (1)
Open a connection to an Arduino connected to a Raspberry Pi and read a string returned by the Arduino:
Read the next byte sent from the Arduino:
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2014 (10.0)
