Call a Wolfram API from Python
Call a Wolfram API from Python
Using a Wolfram notebook...
Create the API
Create a simple APIFunction:

Deploy the API
Deploy the API to the Wolfram Cloud:
Prepare the input parameters
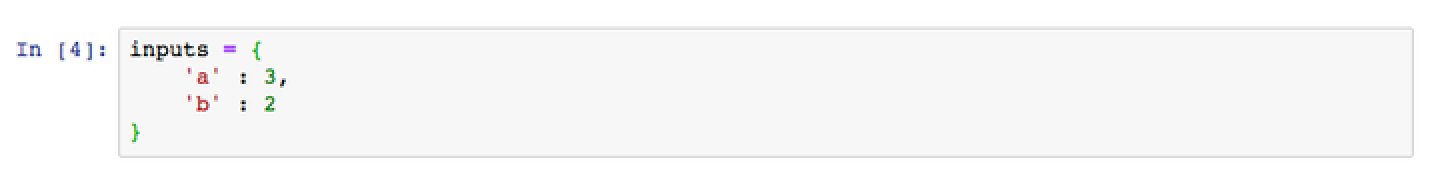
API inputs are passed as named parameters using a Python dictionary:
inputs = {
'a' : 3,
'b' : 2
}
Make the call
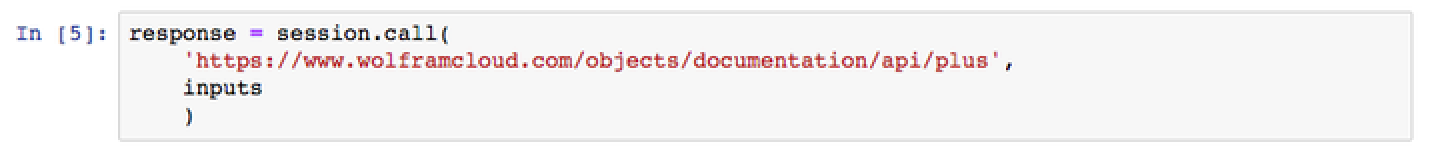
Using an authenticated cloud session, call the API from Python:
response = session.call(
'https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/documentation/api/plus',
inputs
)
- This workflow requires the Wolfram Client Library for Python, installed as described in
 .
. - session is the authenticated cloud session instantiated during this workflow:
 .
.
Get the Response
response.get()
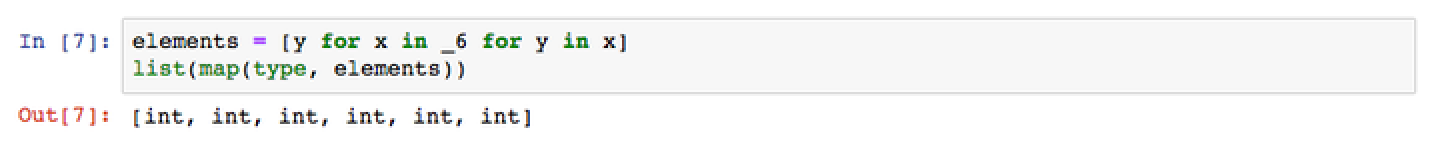
Verify that the type passed to the Wolfram Language is consistent:

Using a Jupyter notebook...
Create the API
Create a simple APIFunction:

Deploy the API
Deploy the API to the Wolfram Cloud:
Prepare the input parameters
API inputs are passed as named parameters using a Python dictionary:
Make the call
Using an authenticated cloud session, call the API from Python:
- This workflow requires the Wolfram Client Library for Python, installed as described in
 .
. - session is the authenticated cloud session instantiated during this workflow:
 .
.
Get the response

Verify that the type passed to Python is consistent: