AiryAi[z]
gives the Airy function ![]() .
.




AiryAi
AiryAi[z]
gives the Airy function ![]() .
.
Details

- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
- The Airy function
![TemplateBox[{z}, AiryAi] TemplateBox[{z}, AiryAi]](Files/AiryAi.en/2.png) is a solution to the differential equation
is a solution to the differential equation 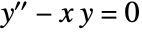 .
. ![TemplateBox[{z}, AiryAi] TemplateBox[{z}, AiryAi]](Files/AiryAi.en/4.png) tends to zero as
tends to zero as 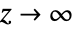 .
. - AiryAi[z] is an entire function of z with no branch cut discontinuities.
- For certain special arguments, AiryAi automatically evaluates to exact values.
- AiryAi can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- AiryAi automatically threads over lists.
- AiryAi can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
Plot over a subset of the reals:
Plot over a subset of the complexes:
Series expansion at the origin:
Series expansion at Infinity:
Scope (42)
Numerical Evaluation (5)
Evaluate numerically to high precision:
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate for complex arguments:
Evaluate AiryAi efficiently at high precision:
Compute worst-case guaranteed intervals using Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Or compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Compute the elementwise values of an array:
Or compute the matrix AiryAi function using MatrixFunction:
Specific Values (4)
Visualization (2)
Function Properties (9)
AiryAi is defined for all real and complex values:
Approximate function range of AiryAi:
AiryAi is an analytic function of x:
AiryAi is neither non-increasing nor non-decreasing:
AiryAi is not injective:
AiryAi is not surjective:
AiryAi is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
AiryAi has no singularities or discontinuities:
AiryAi is neither convex nor concave:
Integration (3)
Series Expansions (5)
Integral Transforms (3)
Function Identities and Simplifications (3)
Simplify the expression to AiryAi:
FunctionExpand tries to simplify the argument of AiryAi:
Function Representations (5)
Integral representation for real argument:
Relationship to Bessel functions:
AiryAi can be represented as a DifferentialRoot:
AiryAi can be represented in terms of MeijerG:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Applications (4)
Solve the Schrödinger equation in a linear potential (e.g. uniform electric field):
Plot the absolute value in the complex plane:
Nested integrals of the square of AiryAi:
Compute the probability density of Map–Airy distribution [MathWorld] in closed form, represented with AiryAi and AiryAiPrime functions:
Properties & Relations (8)
Use FullSimplify to simplify expressions involving Airy functions:
Compare with the output of Wronskian:
FunctionExpand tries to simplify the argument of AiryAi:
Solve the Airy differential equation:
Compare with built-in function AiryAiZero:
AiryAi can be represented as a DifferentialRoot:
Possible Issues (5)
Machine-precision input is insufficient to get a correct answer:
Use arbitrary-precision evaluation instead:
A larger setting for $MaxExtraPrecision can be needed:
Machine-number inputs can give high‐precision results:
Simplifications sometimes hold only in parts of the complex plane:
Parentheses are required when inputting in the traditional form:
Neat Examples (1)
Play a vibrato sound made from a linear combination of AiryAi functions:
See Also
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Related Links
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 2021 (13.0) ▪ 2022 (13.1)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), AiryAi, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AiryAi.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "AiryAi." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AiryAi.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). AiryAi. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AiryAi.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_airyai, author="Wolfram Research", title="{AiryAi}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AiryAi.html}", note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_airyai, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={AiryAi}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AiryAi.html}, note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}