AudioDelay[audio,delay]
creates audio by adding repeated decaying echos to audio spaced by the specified delay.
AudioDelay[audio,delay,feedback]
uses the specified feedback as the amount of signal to preserve during each repetition.
AudioDelay[audio,delay,feedback,mix]
uses mix to control the ratio between original and delayed audio.
AudioDelay[video,…]
add delay to the first audio track in video.


AudioDelay
AudioDelay[audio,delay]
creates audio by adding repeated decaying echos to audio spaced by the specified delay.
AudioDelay[audio,delay,feedback]
uses the specified feedback as the amount of signal to preserve during each repetition.
AudioDelay[audio,delay,feedback,mix]
uses mix to control the ratio between original and delayed audio.
AudioDelay[video,…]
add delay to the first audio track in video.
Details and Options

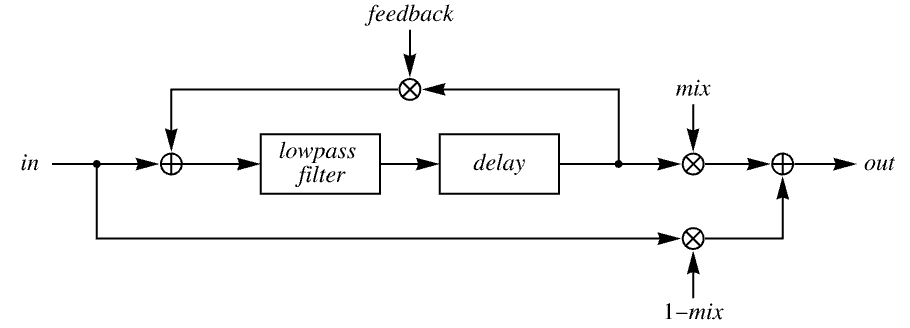
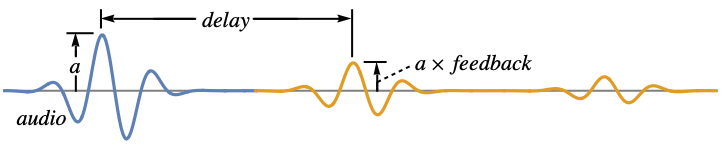
- AudioDelay simulates the effect of a decaying echo. »
- AudioDelay[audio,delay] is equivalent to AudioDelay[audio,delay,0,.5].
- The mixing parameter mix can be any real number between 0 and 1.
- With mix=0, only the original signal is returned; with mix=1, only the delayed signal is returned.
- The feedback parameter can be any real number between
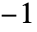 and 1.
and 1. - The AudioType of the returned object is either "Real32" or "Real".
- The following options can be given:
-
Method Automatic the method to use PaddingSize Automatic amount of padding on the right - By default, the input signal is lowpass filtered using an automatic cutoff frequency. Use Method->{"LowpassCutoff"->ω} to specify the cutoff frequency. Using Method->{"LowpassCutoff"->None}, no filtering is performed.
- Use PaddingSize->pad to add pad seconds of padding to the right of the audio signal.
Examples
open all close allScope (5)
Specify the amount of delay using a time quantity:
The feedback controls the amount of decay:
A value of 0 will result in a single repetition:
A negative feedback will alternate the phase:
A value of 1 will cause the repetitions to not decay:
The mix parameter controls the ratio between the original signal and the delayed signal:
Use a mix value of 0 to return the original signal ("dry"):
Use a value of 1 to return the delayed signal ("wet") only:
Use a value between 0 and 1 to control the ratio between the "dry" and "wet" signals:
AudioDelay returns a "Real32" audio signal:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2016), AudioDelay, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AudioDelay.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2016. "AudioDelay." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AudioDelay.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2016). AudioDelay. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AudioDelay.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_audiodelay, author="Wolfram Research", title="{AudioDelay}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AudioDelay.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_audiodelay, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={AudioDelay}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AudioDelay.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}