BinLists[data]
gives lists of the elements of data whose values lie in successive integer bins.
BinLists[data,binspec]
gives lists of the elements of data whose values lie in successive bins specified by binspec.
BinLists[datainds,…]
gives the lists of the labels inds specified by the binning of data.


BinLists
BinLists[data]
gives lists of the elements of data whose values lie in successive integer bins.
BinLists[data,binspec]
gives lists of the elements of data whose values lie in successive bins specified by binspec.
BinLists[datainds,…]
gives the lists of the labels inds specified by the binning of data.
Details



- BinLists drops elements whose values do not correspond to real numbers.
- The following bin-width specifications binspec can be given:
-
dx bins of width dx » {xmin,xmax,dx} bins of width dx from xmin to xmax » {{b1,b2,…}} the intervals [b1,b2), [b2,b3), … » xbins,ybins,… bin specifications for multivariate data understood as {{x1,y1,…},{x2,y2, …},…} » - BinLists[data,dx] takes the bin boundaries to be integer multiples of dx, with the first bin starting at Ceiling[Min[data]-dx,dx] and the last bin ending at Floor[Max[data]+dx,dx].
-

- BinLists[data] is equivalent to BinLists[data,1].
- In BinLists[data,{xmin,xmax,dx}], elements are placed in bin i when their values satisfy
 .
. -
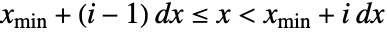
- BinLists[data,{xmin,xmax}] is equivalent to BinLists[data,{xmin,xmax,1}].
- In BinLists[data,{{b1,b2,…}}], elements are put in bin i when their values satisfy
 .
. -
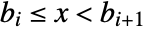
- In the form BinLists[data,{{b1,b2,…}}], the bi at each end can be -Infinity and +Infinity.
- If the bi do not form an increasing sequence, they are automatically sorted by BinLists.
- If data consists of length-n sublists, then n bin specifications must be given, and BinLists[data,…] yields an array of lists of depth n.
- Within each bin, elements appear in the same order as in the original data.
- The data can have the following forms and interpretations:
-
{x1,x2,…} list of real numbers or quantities » {{x1,y1,…},{x2,y2,…},…} list of vectors of the same dimension » SparseArray an array equivalent to Normal[data] » QuantityArray array of column-compatible quantities » TimeSeries, TemporalData,… vector or array of values (the time stamps ignored) » - Labels inds for the input elements xi can be given in the following formats: »
-
{x1,x2,…} use the xi themselves (no labels by default) {x1,x2,…}Automatic use integer labels {x1,x2,…}{v1,v2,…} a rule between all the elements and all the labels {x1v1,x2v2,…} a list of rules between the element xi and its label vi
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (12)
Basic Uses (8)
List squares mod 3 and 5 in two-dimensional unit bins:
List random pairs in bins of width 0.25 in both dimensions:
List multidimensional data in ranges:
Bin data, ignoring values that are not real:
SparseArray data can be used just like dense arrays:
Data with Quantities (3)
Bins of fixed width, minimum and maximum:
The units are compatible for each dimension:
Specify bin width for each dimension:
QuantityArray can be used just like arrays:
Properties & Relations (1)
Possible Issues (4)
Binning intervals are closed on the left:
For data involving quantities, the bin specification must be given in compatible units:
Matrix data must have unit-compatible columns:
The bins obtained using the specification {min,max,dx} may not include all data points:
Specify the min and max so all data points are included in the bin covering:
See Also
BinCounts Cases Union Sort Gather GatherBy Split FindDivisions
Function Repository: BinListsBy HextileBins TileBins
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), BinLists, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BinLists.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "BinLists." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BinLists.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). BinLists. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BinLists.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_binlists, author="Wolfram Research", title="{BinLists}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BinLists.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_binlists, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={BinLists}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/BinLists.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}