CanonicalWarpingDistance[s1,s2]
gives the canonical time warping (CTW) distance between sequences s1 and s2.
CanonicalWarpingDistance[s1,s2,init]
uses init as the initial correspondence between the two sequences.
CanonicalWarpingDistance[s1,s2,init,win]
uses a window win for local search.


CanonicalWarpingDistance
CanonicalWarpingDistance[s1,s2]
gives the canonical time warping (CTW) distance between sequences s1 and s2.
CanonicalWarpingDistance[s1,s2,init]
uses init as the initial correspondence between the two sequences.
CanonicalWarpingDistance[s1,s2,init,win]
uses a window win for local search.
Details and Options


- Canonical time warping (CTW) iteratively performs spatial transformations and dynamic time warping on the reference sequence s1 and the query sequence s2 to find the alignment with minimal distance between sequences.
- The sequences si can be lists of numeric scalars or vectors. In contrast to dynamic time warping, elements of s1 and s2 can be of different dimensions.
- The distance is given by
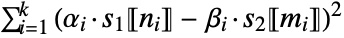 , where s1〚ni〛 and s2〚mi〛 are corresponding elements, and α and β are spatial transformation matrices computed using canonical correlation analysis.
, where s1〚ni〛 and s2〚mi〛 are corresponding elements, and α and β are spatial transformation matrices computed using canonical correlation analysis. - The correspondence giving the computed distance can be obtained using CanonicalWarpingCorrespondence.
- Initial correspondence init should be given in the form of {{n1,…,nk},{m1,…,mk}}, which provides an initial one-to-one correspondence between the elements of s1 and s2.
- Possible settings for the search window win are:
-

Automatic a full search 
r a slanted band window of radius 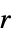

{"SlantedBand",r} a slanted band window of radius 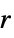

{"Band",r} band window of radius 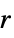 (Sakoe-Chiba)
(Sakoe-Chiba)
{"Parallelogram",a} parallelogram window placed at origin with slopes 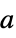 and
and 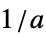 (Itakura)
(Itakura) - The following options are supported:
-
DistanceFunction Automatic distance function used in dynamic time warping MaxIterations Automatic maximal number of iterations Method Automatic the variant of CTW to use - For possible settings of DistanceFunction, see the reference page for WarpingDistance.
- The following options are available through Method->opts:
-
"DimensionsToKeep" Automatic dimensions after projection "EnergyThreshold" Automatic fraction of "energy" to be kept "Lambdas" Automatic regularization values "MatchingIntervals" Automatic whether to match the query to full or part of reference - Possible settings for the "MatchingIntervals" option include:
-
Automatic a full match "Flexible" flexible at both ends "FlexibleEnd" flexible only at the end of the interval
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (9)
Data (6)
Find the distance between two sequences of numerical scalars with different length:
Find the distance between two sequences of vectors:
Find the distance between a sequence of scalars and a sequence of 3D points:
Find the distance between two sequences of quantities with compatible units:
All units are converted to base SI units:
Find the distance between two sequences of quantity vectors with compatible units:
Find the distance between a sequence of quantities and a sequence of scalars:
The scalars are interpreted as if they had a compatible unit from SI base units:
Initial Warping (1)
Options (2)
MaxIterations (2)
By default, the maximal number of iterations is 50:
Decreasing the maximal number of iterations may reduce the timing:
Increasing the maximal number of iterations may yield a smaller distance whenever CTW converges:
Set MaxIterations∞ to find the distance after convergence. CTW may not converge:
Applications (1)
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2016), CanonicalWarpingDistance, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CanonicalWarpingDistance.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2016. "CanonicalWarpingDistance." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CanonicalWarpingDistance.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2016). CanonicalWarpingDistance. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CanonicalWarpingDistance.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_canonicalwarpingdistance, author="Wolfram Research", title="{CanonicalWarpingDistance}", year="2016", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CanonicalWarpingDistance.html}", note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_canonicalwarpingdistance, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={CanonicalWarpingDistance}, year={2016}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/CanonicalWarpingDistance.html}, note=[Accessed: 09-March-2026]}