FindEulerianCycle
finds an Eulerian cycle in the graph g.
FindEulerianCycle[g,k]
finds at most k Eulerian cycles.
FindEulerianCycle[{vw,…},…]
uses rules vw to specify the graph g.
Details
- An Eulerian cycle is a cycle that traverses every edge exactly once.
- FindEulerianCycle returns a list of paths consisting of Eulerian cycles.
- FindEulerianCycle returns the list {} if no Eulerian cycles exist.
- FindEulerianCycle[g] is equivalent to FindEulerianCycle[g,1].
- FindEulerianCycle[g,All] finds all Eulerian cycles in the graph g.
- FindEulerianCycle works with undirected graphs, directed graphs, and multigraphs.
Background & Context
- FindEulerianCycle attempts to find one or more distinct Eulerian cycles, also called Eulerian circuits, Eulerian tours, or Euler tours in a graph. The cycles are returned as a list of edge lists or as {} if none exist. An Eulerian cycle (more properly called a circuit when the cycle is identified using a explicit path with particular endpoints) is a consecutive sequence of distinct edges such that the first and last edge coincide at their endpoints and in which each edge appears exactly once. Eulerian cycles may be used to reconstruct genome sequences, construct de Bruijn sequences, and to find optimal conference scheduling.
- FindEulerianCycle[g,k] attempts to find k Eulerian cycles, where the count specification k may be omitted (in which case it is taken as 1), may be a positive integer, or may be All. Eulerian cycles need not be simple cycles, i.e. there can be a repeated vertex in a cycle (unlike Hamiltonian cycles, which are always simple).
- A graph possessing an Eulerian cycle is known as an Eulerian graph. However, some care is needed in interpreting the term, since some authors define an Euler (as opposed to "Eulerian") graph as a different object, namely a graph for which all vertices are of even degree. The latter definition is motivated by Euler's correct (but unproved by him) observation that a connected simple graph possesses an Eulerian circuit if and only if it has no vertices of odd degree. Eulerian cycles are therefore mathematically easier to study than Hamiltonian cycles. While the number of connected Euler graphs on
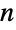 nodes is equal to the number of connected Eulerian graphs on
nodes is equal to the number of connected Eulerian graphs on 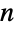 nodes, the counts are different for disconnected graphs since there exist disconnected graphs having multiple disjoint cycles with each node even but for which no single cycle passes through all edges.
nodes, the counts are different for disconnected graphs since there exist disconnected graphs having multiple disjoint cycles with each node even but for which no single cycle passes through all edges. - EulerianGraphQ can be used to determine if a graph is Eulerian. Functions for finding other sorts of cycles include FindCycle and FindHamiltonianCycle.
Examples
open allclose allScope (8)
FindEulerianCycle works with undirected graphs:
Use rules to specify the graph:
FindEulerianCycle returns an empty result for non-Eulerian graphs:
FindEulerianCycle works with large graphs:
Applications (7)
The seven bridges of the city of Königsberg over the river Pregel cannot all be traversed in a single trip without doubling back, with the additional requirement that the trip ends in the same place it began:
Trace out the figure of an envelope without lifting the pen and without going over the same line twice:
Since there are two odd-degree vertices, an augmented Eulerian graph is constructed by joining the odd-degree vertices via a new vertex (to avoid multiple edges):
Find an Eulerian cycle in the augmented graph:
Rotate the edges of the cycle until the edges involving the vertex ![]() become the last ones:
become the last ones:
Find the most optimal scheduling of a conference room for the following meetings:
The graph of participants with edges connecting attendees of the same meeting:
There is no optimal schedule allowing two consecutive meetings to share a participant:
Add virtual meetings between participants with an odd number of meetings:
Graph-based assembly of a circular genome "ATGGCGTGCA" with vertices as (k-1)-mers and edges as k-mers:
Construct a k-ary de Bruijn sequence from an Eulerian cycle:
Find the order of vertices visited along a directed cycle:
Pick the source vertex of each edge:
Properties & Relations (6)
Use GraphData for an extensive collection of Eulerian graphs:
Test whether a graph has an Eulerian cycle using EulerianGraphQ:
A connected undirected graph with vertices of even degree has an Eulerian cycle:
An undirected graph has an Eulerian cycle if it can be decomposed into edge-disjoint cycles:
The line graph of an undirected Eulerian graph has an Eulerian cycle:
A directed graph with in-degree and out-degree equal for each vertex has an Eulerian cycle:
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), FindEulerianCycle, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindEulerianCycle.html (updated 2015).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "FindEulerianCycle." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2015. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindEulerianCycle.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). FindEulerianCycle. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindEulerianCycle.html