returns an n×n discrete sine transform matrix of type 2.
FourierDSTMatrix[n,m]
returns an n×n discrete sine transform matrix of type m.


FourierDSTMatrix
returns an n×n discrete sine transform matrix of type 2.
FourierDSTMatrix[n,m]
returns an n×n discrete sine transform matrix of type m.
Details and Options

- Each entry Frs of the discrete sine transform matrix of type m is computed as:
-
1. DST-I 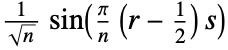
2. DST-II 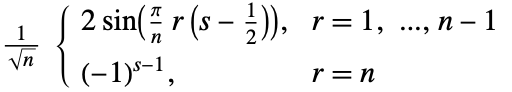
3. DST-III 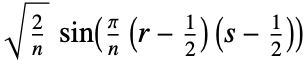
4. DST-IV 
- The discrete sine transform matrices of types 1, 2, 3 and 4 have inverses of type 1, 3, 2 and 4, respectively. »
- Rows of the FourierDSTMatrix are basis sequences of the discrete sine transform.
- The result of FourierDSTMatrix[n].list is equivalent to FourierDST[list] when list has length n. However, the computation of FourierDST[list] is much faster and has less numerical error. »
- For types 1 and 4, the option TargetStructure is supported, which specifies the structure of the returned matrix. Possible settings for TargetStructure include:
-
Automatic automatically choose the representation returned "Dense" represent the matrix as a dense matrix "Hermitian" represent the matrix as a Hermitian matrix "Orthogonal" represent the matrix as an orthogonal matrix "Symmetric" represent the matrix as a symmetric matrix "Unitary" represent the matrix as a unitary matrix - FourierDSTMatrix[…,TargetStructureAutomatic] is equivalent to FourierDSTMatrix[…,TargetStructure"Dense"].
- FourierDSTMatrix[…,WorkingPrecision->p] gives a matrix with entries of precision p.
Examples
open all close allOptions (2)
Applications (1)
Properties & Relations (2)
A DST matrix multiplied by a vector is equivalent to the discrete sine transform of that vector:
FourierDST is much faster than the matrix-based computation:
A discrete sine transform matrix of type 1 is its own inverse:
A discrete sine transform matrix of type 3 is an inverse of the type 2 matrix:
A discrete sine transform matrix of type 4 is its own inverse:
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), FourierDSTMatrix, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FourierDSTMatrix.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "FourierDSTMatrix." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FourierDSTMatrix.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). FourierDSTMatrix. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FourierDSTMatrix.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_fourierdstmatrix, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FourierDSTMatrix}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FourierDSTMatrix.html}", note=[Accessed: 03-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_fourierdstmatrix, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FourierDSTMatrix}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FourierDSTMatrix.html}, note=[Accessed: 03-March-2026]}