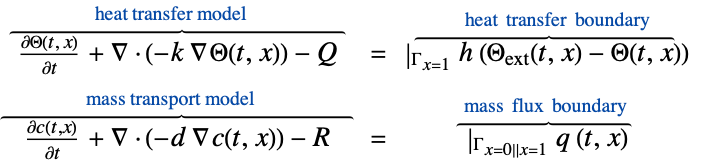HeatTransferValue[pred,vars,pars]
represents a thermal transfer boundary condition for PDEs with predicate pred indicating where it applies, with model variables vars and global parameters pars.
HeatTransferValue[pred,vars,pars,lkey]
represents a thermal transfer boundary condition with local parameters specified in pars[lkey].


HeatTransferValue
HeatTransferValue[pred,vars,pars]
represents a thermal transfer boundary condition for PDEs with predicate pred indicating where it applies, with model variables vars and global parameters pars.
HeatTransferValue[pred,vars,pars,lkey]
represents a thermal transfer boundary condition with local parameters specified in pars[lkey].
Details



- HeatTransferValue specifies a boundary condition for HeatTransferPDEComponent and is used as part of the modeling equation:
- HeatTransferValue is typically used to model the effect of a cooling or heating flow outside the simulation domain. Common examples include a heat sink.
- HeatTransferValue models thermal energy transferred across a boundary with dependent variable temperature
 [
[![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "K", kelvins, "Kelvins"}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "K", kelvins, "Kelvins"}, QuantityTF]](Files/HeatTransferValue.en/4.png) ], independent variables
], independent variables 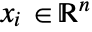 in [
in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "m", meters, "Meters"}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "m", meters, "Meters"}, QuantityTF]](Files/HeatTransferValue.en/6.png) ] and time variable
] and time variable 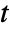 in [
in [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "s", seconds, "Seconds"}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "s", seconds, "Seconds"}, QuantityTF]](Files/HeatTransferValue.en/8.png) ].
]. - Stationary variables vars are vars={Θ[x1,…,xn],{x1,…,xn}}.
- Time-dependent variables vars are vars={Θ[t,x1,…,xn],t,{x1,…,xn}}.
- The non-conservative time-dependent heat transfer model HeatTransferPDEComponent is based on a convection-diffusion model with mass density
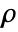 , specific heat capacity
, specific heat capacity 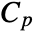 , thermal conductivity
, thermal conductivity 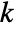 , convection velocity vector
, convection velocity vector 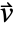 and heat source
and heat source 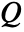 :
: - The heat transfer value HeatTransferValue with heat transfer coefficient
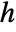 in units of [
in units of [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"W", , "/(", , {"m", ^, 2}, , "K", , ")"}, watts per meter squared kelvin, {{(, "Watts", )}, /, {(, {{"Meters", ^, 2}, , "Kelvins"}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"W", , "/(", , {"m", ^, 2}, , "K", , ")"}, watts per meter squared kelvin, {{(, "Watts", )}, /, {(, {{"Meters", ^, 2}, , "Kelvins"}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/HeatTransferValue.en/16.png) ] and external temperature
] and external temperature 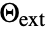 [
[![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "K", kelvins, "Kelvins"}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "K", kelvins, "Kelvins"}, QuantityTF]](Files/HeatTransferValue.en/18.png) ] and boundary unit normal
] and boundary unit normal 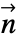 models:
models: - Model parameters pars as specified for HeatTransferPDEComponent.
- The following additional model parameters pars can be given:
-
parameter default symbol "AmbientTemperature" - 0
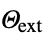 , ambient temperature [
, ambient temperature [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "K", kelvins, "Kelvins"}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], "K", kelvins, "Kelvins"}, QuantityTF]](Files/HeatTransferValue.en/23.png) ]
]"HeatTransferCoefficient" 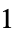
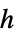 , heat transfer coefficient [
, heat transfer coefficient [![TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"W", , "/(", , {"m", ^, 2}, , "K", , ")"}, watts per meter squared kelvin, {{(, "Watts", )}, /, {(, {{"Meters", ^, 2}, , "Kelvins"}, )}}}, QuantityTF] TemplateBox[{InterpretationBox[, 1], {"W", , "/(", , {"m", ^, 2}, , "K", , ")"}, watts per meter squared kelvin, {{(, "Watts", )}, /, {(, {{"Meters", ^, 2}, , "Kelvins"}, )}}}, QuantityTF]](Files/HeatTransferValue.en/26.png) ]
] - To localize model parameters, a key lkey can be specified, and values from association pars[lkey] are used for model parameters.
- All model parameters may depend on any of
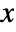 ,
, 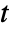 and
and  , as well as other dependent variables.
, as well as other dependent variables. - HeatTransferValue is a special case of HeatFluxValue.
- HeatTransferValue evaluates to a generalized NeumannValue.
- The boundary predicate pred can be specified as in NeumannValue.
- If the HeatTransferValue depends on parameters
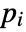 that are specified in the association pars as …,keypi…,pivi,…, the parameters
that are specified in the association pars as …,keypi…,pivi,…, the parameters 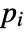 are replaced with
are replaced with 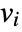 .
.
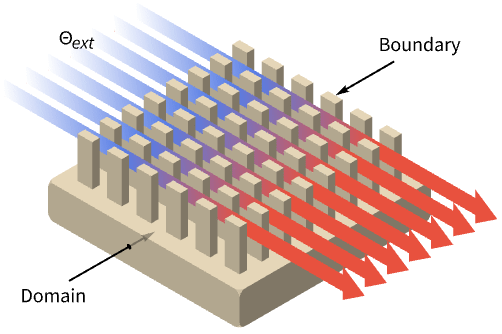
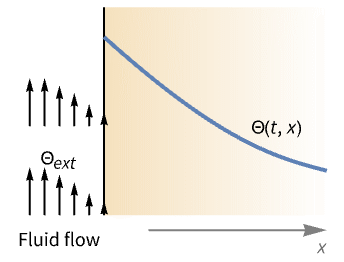
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Set up a thermal convection boundary condition:
Model a temperature field with heat transfer boundary:
Set up the heat transfer model variables ![]() :
:
Specify heat transfer model parameters mass density ![]() , specific heat capacity
, specific heat capacity ![]() and thermal conductivity
and thermal conductivity ![]() :
:
Specify boundary condition parameters with an external flow temperature ![]() of 10 °C and a heat transfer coefficient
of 10 °C and a heat transfer coefficient ![]() of
of ![]() :
:
Scope (4)
Basic Examples (2)
Define model variables vars for a transient acoustic pressure field with model parameters pars and a specific boundary condition parameter:
Define model variables vars for a transient acoustic pressure field with model parameters pars and multiple specific parameter boundary conditions:
2D (1)
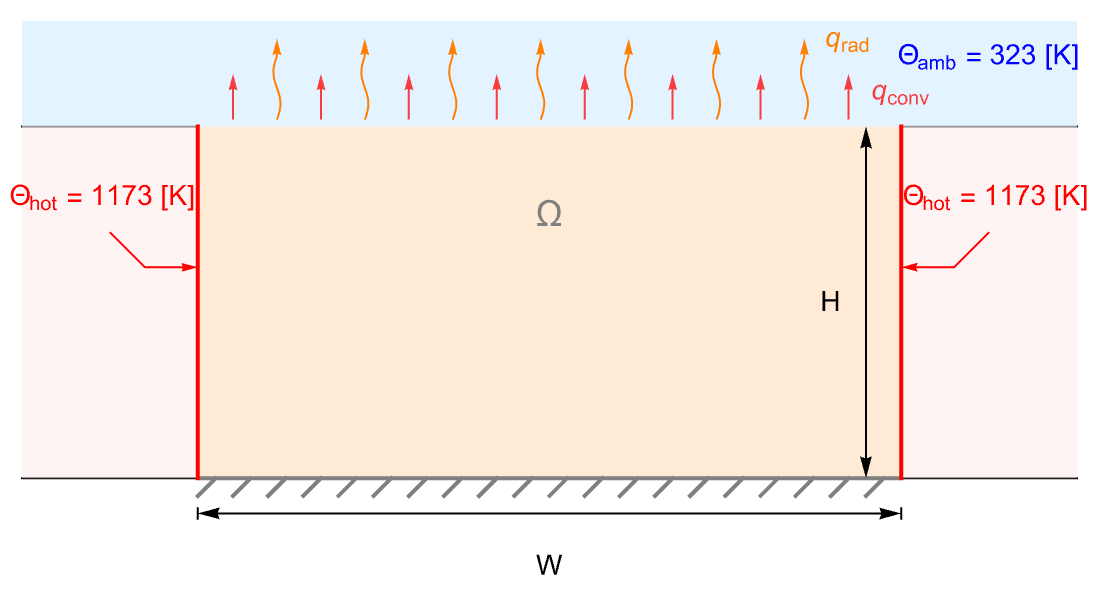
Model a ceramic strip that is embedded in a high-thermal-conductive material. The side boundaries of the strip are maintained at a constant temperature ![]() . The top surface of the strip is losing heat via both heat convection and heat radiation to the ambient environment at
. The top surface of the strip is losing heat via both heat convection and heat radiation to the ambient environment at ![]() . The bottom boundary, however, is assumed to be thermally insulated:
. The bottom boundary, however, is assumed to be thermally insulated:
Model a temperature field and the thermal radiation and thermal transfer with:
Set up the heat transfer model variables ![]() :
:
Set up a rectangular domain with a width of ![]() and a height of
and a height of ![]() :
:
Specify thermal conductivity ![]() :
:
Set up temperature surface boundary conditions ![]() at the left and right boundaries:
at the left and right boundaries:
Set up a heat transfer boundary condition on the top surface:
Also set up a thermal radiation boundary condition on the top surface:
Coupled Equations (1)
Solve a coupled heat transfer and mass transport model with a thermal transfer value and a mass flux value on the boundary:
Set up the heat transfer mass transport model variables ![]() :
:
Specify heat transfer and mass transport model parameters, heat source ![]() , thermal conductivity
, thermal conductivity ![]() , mass diffusivity
, mass diffusivity ![]() and mass source
and mass source ![]() :
:
Specify boundary condition parameters for a thermal convection value with an external flow temperature ![]() of 1000 K and a heat transfer coefficient
of 1000 K and a heat transfer coefficient ![]() of
of ![]() :
:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), HeatTransferValue, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HeatTransferValue.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "HeatTransferValue." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HeatTransferValue.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). HeatTransferValue. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HeatTransferValue.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_heattransfervalue, author="Wolfram Research", title="{HeatTransferValue}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HeatTransferValue.html}", note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_heattransfervalue, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={HeatTransferValue}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HeatTransferValue.html}, note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}