ImageFileScan[f,inputfile]
applies the function f to the list of channel values for each pixel of the image stored in inputfile.


ImageFileScan
ImageFileScan[f,inputfile]
applies the function f to the list of channel values for each pixel of the image stored in inputfile.
Details and Options

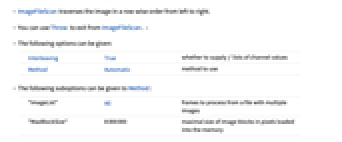
- ImageFileScan can be used to read and process successive pixel data from a very large image file whose size could exceed available memory.
- The channel values supplied to f are normally in the range 0 to 1, regardless of the underlying type used in the Image object.
- ImageFileScan[f,…] discards the results of applying f to the pixels. Unlike ImageFileApply, ImageFileScan does not create a new file and returns Null.
- ImageFileScan is useful in carrying out an operation on individual pixels where the operation has a "side effect", such as making an assignment.
- ImageFileScan works with TIFF, JPEG, and PNG files.
- ImageFileScan works on images with any number of channels.
- The image file inputfile can be given as a string or a File object.
- ImageFileScan traverses the image in a row-wise order from left to right.
- You can use Throw to exit from ImageFileScan. »
- The following options can be given:
-
Interleaving True whether to supply f lists of channel values Method Automatic method to use - The following suboptions can be given to Method:
-
"ImageList" All frames to process from a file with multiple images "MaxBlockSize" 8000000 maximal size of image blocks in pixels loaded into the memory - The value of the option "MaxBlockSize" may be exceeded if it is smaller than the smallest block supported for the input file.
Examples
open all close allScope (2)
Generalizations & Extensions (1)
Throw works inside ImageFileScan:
Properties & Relations (1)
Compute the total intensity of an out-of-core image:
If the data fits into the memory, this is the same as Total on the imported image:
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2012 (9.0) | Updated in 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2015 (10.1) ▪ 2016 (11.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), ImageFileScan, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageFileScan.html (updated 2016).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "ImageFileScan." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2016. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageFileScan.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). ImageFileScan. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageFileScan.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_imagefilescan, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ImageFileScan}", year="2016", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageFileScan.html}", note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_imagefilescan, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ImageFileScan}, year={2016}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ImageFileScan.html}, note=[Accessed: 28-February-2026]}