MeshShading
is an option for plotting functions that gives lists of colors to use for regions between mesh divisions.
Details

- MeshShading->{c1,c2,…} specifies that directives ci should be used cyclically for each of the n+1 regions defined by n mesh divisions.
- MeshShading->{{c11,c12,…},{c21,…},…} specifies that the cij should be used cyclically for the i,j
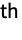 patch defined by two mesh functions.
patch defined by two mesh functions. - If k mesh functions are specified, the setting for MeshShading should be an array of depth k.
- The setting for MeshShading can be a SparseArray object.
- The default setting MeshShading->None specifies that no additional directives associated with mesh regions should be added.
- The elements of the MeshShading array should be color directives such as RGBColor, Hue, or named colors such as Red and Blue. They can also include Opacity.
- In cases where regions defined by MeshShading are surfaces, directives such as EdgeForm, FaceForm, and Specularity can be used.
- When the regions defined by MeshShading are lines, directives such as Thickness and Dashing can also be used.
- Directives can be combined using Directive[g1,g2,…].
Examples
Basic Examples (4)
Style the areas between mesh lines:
Alternate colors along a curve:
Use MeshShading with ColorFunction:
Use MeshShading to remove portions of a surface:
Wolfram Research (2007), MeshShading, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MeshShading.html.
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), MeshShading, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MeshShading.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "MeshShading." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MeshShading.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). MeshShading. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MeshShading.html