ParallelSelect[data,crit]
picks out all elements ei of data for which crit[ei] is True, in parallel.


ParallelSelect
ParallelSelect[data,crit]
picks out all elements ei of data for which crit[ei] is True, in parallel.
Details and Options
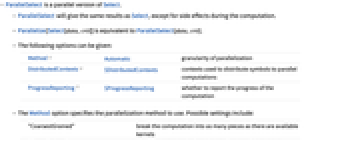

- ParallelSelect is a parallel version of Select.
- ParallelSelect will give the same results as Select, except for side effects during the computation.
- Parallelize[Select[data,crit]] is equivalent to ParallelSelect[data,crit].
- The following options can be given:
-
Method Automatic granularity of parallelization DistributedContexts $DistributedContexts contexts used to distribute symbols to parallel computations ProgressReporting $ProgressReporting whether to report the progress of the computation - The Method option specifies the parallelization method to use. Possible settings include:
-
"CoarsestGrained" break the computation into as many pieces as there are available kernels "FinestGrained" break the computation into the smallest possible subunits "EvaluationsPerKernel"->e break the computation into at most e pieces per kernel "ItemsPerEvaluation"->m break the computation into evaluations of at most m subunits each Automatic compromise between overhead and load balancing - Method->"CoarsestGrained" is suitable for computations involving many subunits, all of which take the same amount of time. It minimizes overhead but does not provide any load balancing.
- Method->"FinestGrained" is suitable for computations involving few subunits whose evaluations take different amounts of time. It leads to higher overhead but maximizes load balancing.
- The DistributedContexts option specifies which symbols appearing in expr have their definitions automatically distributed to all available kernels before the computation.
- The default value is DistributedContexts:>$DistributedContexts with $DistributedContexts:=$Context, which distributes definitions of all symbols in the current context but does not distribute definitions of symbols from packages.
- The ProgressReporting option specifies whether to report the progress of the parallel computation.
- The default value is ProgressReporting:>$ProgressReporting.
Examples
open all close allOptions (5)
DistributedContexts (2)
Method (1)
ProgressReporting (2)
Do not show a temporary progress report:
Use Method"FinestGrained" for the most accurate progress report:
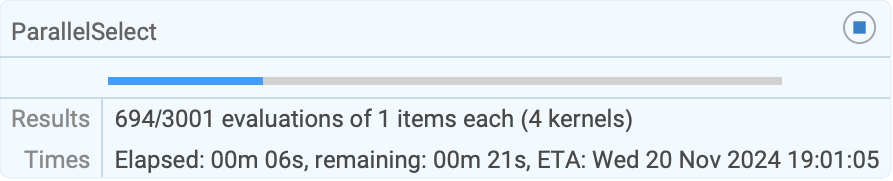
| |
Possible Issues (2)
The optional third argument n of Select cannot be parallelized:
Returning properties of the selected elements does not parallel correctly:
The result depends on the number of kernels and the parallelization method used:
See Also
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2025), ParallelSelect, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParallelSelect.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "ParallelSelect." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParallelSelect.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). ParallelSelect. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParallelSelect.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_parallelselect, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ParallelSelect}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParallelSelect.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_parallelselect, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ParallelSelect}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ParallelSelect.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}