RankedMin
RankedMin[list,n]
gives the n![]() smallest element in list.
smallest element in list.
RankedMin[list,-n]
gives the n![]() largest element in list.
largest element in list.
Details
- RankedMin yields a definite result if all its arguments are real numbers.
- RankedMin[{x1,…,xm},n] is often indicated using
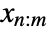 or
or 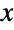 .
. - RankedMin[{x1,…,xm},1] is equivalent to Min[{x1,…,xm}]. »
- RankedMin[{x1,…,xm},-1] is equivalent to Max[{x1,…,xm}].
- RankedMin[{x1,…,xm},m] is equivalent to Max[{x1,…,xm}]. »
- RankedMin[{x1,…,xm},n] is equivalent to Quantile[{x1,…,xm},n/m]. »
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (25)
Numerical Evaluation (7)
Evaluate the second smallest of three numbers:
The fourth smallest—i.e. the largest—of four numbers:
The second largest of five numbers:
The fourth largest of five numbers:
The fifth largest—i.e. the smallest—of five numbers:
Evaluate efficiently at high precision:
RankedMin of WeightedData ignores the weights:
Specific Values (4)
Visualization (3)
Function Properties (8)
RankedMin is only defined for real-valued inputs:
The range of RankedMin is real numbers:
Basic symbolic simplification is done automatically:
Multi-argument ranked RankedMin is generally not an analytic function:
It will have singularities where the functions cross, but it will be continuous:
Applications (8)
Plot the bivariate RankedMin functions:
Plot the contours of bivariate and trivariate RankedMin functions:
RankedMin[{y1,…,yn,x},k] as a function of x:
Compute the expectation of the second smallest (median) variable:
Alternatively, use OrderDistribution:
Compute the probability of the second smallest variable being less than 1:
Show that OrderDistribution is a special case of TransformedDistribution:
Find the height of the third shortest child in a class:
Properties & Relations (6)
RankedMin[{x1,…,xm},1] is equivalent to Min[x1,…,xm]:
RankedMin[{x1,…,xm},m] is equivalent to Max[x1,…,xm]:
RankedMin[{x1,…,xm},n] is equivalent to RankedMax[{x1,…,xm},m-n+1]:
RankedMin[{x1,…,xm},n] is equivalent to Quantile[{x1,…,xm},n/m]:
RankedMin[{x1,…,xm},n] is equivalent to Sort[{x1,…,xm}]〚n〛:
The equivalent Piecewise function has disjoint piecewise case domains:
Algebraically prove the piecewise case domains are disjoint:
Algebraically prove the piecewise case domains are pairwise disjoint:
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), RankedMin, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RankedMin.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "RankedMin." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RankedMin.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). RankedMin. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RankedMin.html