"ExtensibleVector" (Data Structure)
"ExtensibleVector"
represents a dynamically extensible vector where the elements are general expressions.
Details


- An extensible vector is useful for continuously appending and prepending elements, as well as for efficient element extraction and updating.
-
CreateDataStructure[ "ExtensibleVector"] create a new empty "ExtensibleVector" CreateDataStructure[ "ExtensibleVector",elems] create a new "ExtensibleVector"containing elems Typed[x,"ExtensibleVector"] give x the type "ExtensibleVector" - For a data structure of type "ExtensibleVector", the following operations can be used:
-
ds["Append",x] append x to ds time: O(1) ds["Copy"] return a copy of ds time: O(n) ds["Drop",i] drop the i 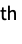 part of ds
part of dstime: O(n) ds["DropAll"] drop all the elements from ds time: O(n) ds["DropLast"] drop the last element of ds time: O(1) ds["Elements"] return a list of the elements of ds time: O(n) ds["EmptyQ"] True, if ds has no elements time: O(1) ds["Fold",fun,init] apply fun to the elements of ds, starting with init, accumulating a result time: O(n) ds["Insert",x,i ] insert x into ds at position i time: O(1) ds["JoinBack",elems ] join elems to the back of ds time: O(nelems) ds["JoinFront",elems ] join elems to the front of ds time: O(nelems) ds["Length"] the number of elements stored in ds time: O(1) ds["Part",i] give the i 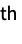 part of ds
part of dstime: O(1) ds["Prepend",x] prepend x to ds time: O(1) ds["SetPart",i,elem] update the i 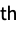 part of ds
part of dstime: O(1) ds["SwapPart",i,j] swap the i 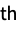 and j
and j parts of ds
parts of dstime: O(1) ds["Visualization"] return a visualization of ds time: O(n) - The following functions are also supported:
-
dsi===dsj True, if dsi equals dsj ds["Part",i]=val set i  element of ds to val
element of ds to valFullForm[ds] full form of ds Information[ds] information about ds InputForm[ds] input form of ds Normal[ds] convert ds to a normal expression
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
A new "ExtensibleVector" can be created with CreateDataStructure:
Return an expression version of ds:
Scope (1)
Information (1)
A new "ExtensibleVector" can be created with CreateDataStructure:
Applications (11)
Reverse (1)
Bubble Sort (1)
Insertion Sort (1)
Quicksort (1)
Merge Sort (1)
Heapsort (1)
Timsort (1)
Fisher–Yates Shuffle (1)
Palindrome (1)
Quickselect (1)
Heap (1)
A heap is a tree-based data structure where the value stored at children is smaller than that stored in their parents (for a min heap). It is commonly used to implement a priority queue and typically implemented with an array rather than a tree.
The following converts an array into a heap:
A sample data structure to use:
This converts the array into a heap; it is hard to see the heap property:
This function generates a tree:
A visualization makes it easier to see the min heap property:
Properties & Relations (2)
"FixedArray" (1)
Many algorithms that work for "ExtensibleVector" also work for "FixedArray".
"DynamicArray" (1)
Many algorithms that work for "ExtensibleVector" also work for "DynamicArray".
See Also
CreateDataStructure DataStructure
Data Structures: FixedArray DynamicArray LinkedList DoublyLinkedList RingBuffer
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2021 (13.0)