ControllerState["c"]
gives the state of the control c for the first connected controller device on which it is supported.
ControllerState[{"c1","c2",…}]
gives the states of several controls.
ControllerState[id,"c"]
gives the state of control c for controller devices with the specified identifier.
ControllerState[id,{"c1","c2",…}]
gives the states of several controls for several controller devices.


ControllerState
ControllerState["c"]
gives the state of the control c for the first connected controller device on which it is supported.
ControllerState[{"c1","c2",…}]
gives the states of several controls.
ControllerState[id,"c"]
gives the state of control c for controller devices with the specified identifier.
ControllerState[id,{"c1","c2",…}]
gives the states of several controls for several controller devices.
Details and Options

- Dynamic[ControllerState[…]] gives continually updated current controller states.
- Typical control names include:
-
"X" or "X1" x primary 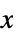 value
value "Y" or "Y1" y primary 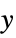 value
value"Z" or "Z1" z primary 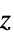 value
value"XY" or "XY1" {x,y} primary 2-axis controller value "XYZ" or "XYZ1" {x,y,z} primary 3-axis controller value "X2", "Y2", "XY2", etc. x, y, {x,y}, etc. values from a secondary controller "B1", "B2", etc. b1, b2, etc. button states - The following special control names are also possible:
-
"Axes" a list of all supported axis-like controls "Buttons" a list of all supported button-like controls "Controls" a list of all supported controls "Hardware" information on the controller device hardware "Mapping" rules for Wolfram System mappings of controls "Rules" rules for the settings of all controls - ControllerState always gives absolute instantaneous control states; it does not give relative or cyclic control states of the type available in Manipulate.
- If no explicit controller identifier id is given, the controller used will be the first one found on the list specified by the option ControllerPath that supports all the controls "ci" requested.
- Identifiers for controllers can be the following:
-
"name" device name from ControllerInformation "class" device class specifier n raw device index from ControllerInformation All all devices supporting the requested controls - Possible device class identifiers include:
-
"Gamepad" controller typically including two analog controls "Joystick" controller typically including one primary analog control "Detachable" controller not built into a computer "BuiltIn" controller built into a computer - If a requested control value is not available, ControllerState returns $Failed for that value.
Examples
open all close allScope (3)
Acquire a list of all button controls supported by the device:
Specify which controller type should be used:
If no device of that type is attached, $Failed is returned:
Options (1)
Properties & Relations (3)
The controls for Manipulate are automatically linked to a controller:
Bind x to the X controller when your selection contains the output:
ControllerInformation can be used to find a device name:
Tech Notes
Related Workflows
- Control Interactive Content with a Gamepad
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), ControllerState, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ControllerState.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "ControllerState." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ControllerState.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). ControllerState. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ControllerState.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_controllerstate, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ControllerState}", year="2007", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ControllerState.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_controllerstate, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ControllerState}, year={2007}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ControllerState.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}