Erfc[z]
gives the complementary error function ![]() .
.




Erfc
Erfc[z]
gives the complementary error function ![]() .
.
Details
- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
- Erfc[z] is given by
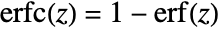 .
. - For certain special arguments, Erfc automatically evaluates to exact values.
- Erfc can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- Erfc automatically threads over lists.
- Erfc can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (5)
Plot over a subset of the reals:
Plot over a subset of the complexes:
Series expansion at the origin:
Series expansion at Infinity:
Scope (40)
Numerical Evaluation (6)
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate for complex arguments:
Evaluate Erf efficiently at high precision:
Compute worst-case guaranteed intervals using Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Or compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Compute the elementwise values of an array:
Or compute the matrix Erfc function using MatrixFunction:
Specific Values (3)
Visualization (2)
Function Properties (9)
Erfc is defined for all real and complex values:
Erfc takes all real values between 0 and 2:
Erfc has the mirror property ![]() :
:
Erfc is an analytic function of x:
It has no singularities or discontinuities:
Erfc is nonincreasing:
Erfc is injective:
Erfc is not surjective:
Erfc is non-negative:
Erfc is neither convex nor concave:
Series Expansions (4)
Integral Transforms (3)
Function Identities and Simplifications (3)
Use FunctionExpand to convert to other functions:
Integral definition of Erfc:
Function Representations (4)
Erfc can be represented as a DifferentialRoot:
Erfc can be represented in terms of MeijerG:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Applications (5)
The CDF of NormalDistribution can be expressed in terms of the complementary error function:
The probability that a random value is greater than ![]() :
:
The solution of the heat equation for a piecewise‐constant initial condition:
A check that the solution fulfills the heat equation:
The plot of the solution for different times:
Define the scaled complementary error function using HermiteH:
Interference pattern at the edge of a shadow:
The lifetime of a device follows a Birnbaum–Saunders distribution. Find the reliability of the device:
The hazard function has the horizontal asymptote ![]() :
:
Find the reliability of two such devices in series:
Properties & Relations (3)
Use FunctionExpand to convert to other functions:
Compose with inverse functions:
Solve a transcendental equation:
Possible Issues (3)
Neat Examples (1)
A continued fraction whose partial numerators are consecutive integers:
Its limit can be expressed in terms of Erfc:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
Related Links
History
Introduced in 1991 (2.0) | Updated in 2021 (13.0) ▪ 2022 (13.1)
Text
Wolfram Research (1991), Erfc, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Erfc.html (updated 2022).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1991. "Erfc." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2022. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Erfc.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1991). Erfc. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Erfc.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_erfc, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Erfc}", year="2022", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Erfc.html}", note=[Accessed: 18-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_erfc, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Erfc}, year={2022}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Erfc.html}, note=[Accessed: 18-February-2026]}