FindFormula[data]
finds a pure function that approximates data.
FindFormula[data,x]
finds a symbolic function of the variable x that approximates data.
FindFormula[data,x,n]
finds up to n functions that approximate data.
FindFormula[data,x,n,prop]
returns up to n best functions associated with property prop.
FindFormula[data,x,n,{prop1,prop2,…}]
returns up to n best functions associated with properties prop1, prop2, etc.


FindFormula
FindFormula[data]
finds a pure function that approximates data.
FindFormula[data,x]
finds a symbolic function of the variable x that approximates data.
FindFormula[data,x,n]
finds up to n functions that approximate data.
FindFormula[data,x,n,prop]
returns up to n best functions associated with property prop.
FindFormula[data,x,n,{prop1,prop2,…}]
returns up to n best functions associated with properties prop1, prop2, etc.
Details and Options

- The data should be either an array of the form {{x1,y1},{x2,y2},…} or {y1,y2,…}, or a TimeSeries object.
- Data of the form {y1,y2,…} is equivalent to data of the form {{1,y1},{2,y2},…}.
- FindFormula[data,x,n,All] creates a Dataset object with all possible properties.
- Properties supported include:
-
"Score" internal score "Complexity" complexity of the function "Error" mean squared error All all the previous properties - The following options can be given:
-
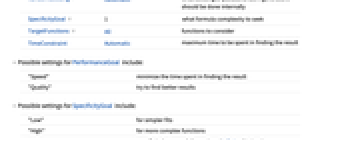
PerformanceGoal Automatic aspect of performance to optimize RandomSeeding Automatic what seeding of pseudorandom generators should be done internally SpecificityGoal 1 - what formula complexity to seek
TargetFunctions All functions to consider TimeConstraint Automatic maximum time to be spent in finding the result - Possible settings for PerformanceGoal include:
-
"Speed" minimize the time spent in finding the result "Quality" try to find better results - Possible settings for SpecificityGoal include:
-
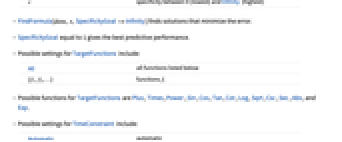
"Low" for simpler fits "High" for more complex functions s specificity between 0 (lowest) and Infinity (highest) - FindFormula[data,x,SpecificityGoal->Infinity] finds solutions that minimize the error.
- SpecificityGoal equal to 1 gives the best predictive performance.
- Possible settings for TargetFunctions include:
-
All all functions listed below { 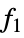 ,
,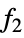 ,…}
,…}functions 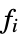
- Possible functions for TargetFunctions are Plus, Times, Power, Sin, Cos, Tan, Cot, Log, Sqrt, Csc, Sec, Abs, and Exp.
- Possible settings for TimeConstraint include:
-
Automatic automatic t maximum t seconds - Possible settings for RandomSeeding include:
-
Automatic automatically reseed every time the function is called Inherited use externally seeded random numbers seed use an explicit integer or strings as a seed
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Make a table of values of the function x Sin[x]:
FindFormula finds a formula that generates the data:
Plot the exponents of known Mersenne primes:
Scope (3)
Generate data with normally distributed noise:
Find the first 5 best functions that approximate data:
Visualize the fitted functions with the data:
Generate data with normally distributed noise:
Visualize the dataset for the first 5 functions that approximate data:
Generate data with normally distributed noise:
Look at the first 300 fits and plot their score as functions of the errors and complexity for different settings of SpecificityGoal:
Options (4)
PerformanceGoal (1)
Generate data with normally distributed noise:
Find the best function that approximates data with its internal score:
Find the best function that approximates data using PerformanceGoal with its internal score:
RandomSeeding (1)
Generate data with normally distributed noise:
Compare different evaluations of FindFormula and notice how they differ:
Use the option RandomSeeding to avoid having different results:
SpecificityGoal (1)
Generate data with normally distributed noise:
Find the best functions that approximate data with their errors using different values of SpecificityGoal:
TargetFunctions (1)
Generate data with normally distributed noise:
Find the best function that approximates data:
Find the best function that approximates data using TargetFunctions:
Applications (3)
Population Growth (1)
Differential Equation (1)
Orbital Mechanics (1)
Plot the orbital periods of planets vs. their semimajor axes:
Find the best simple function describing the orbital radius in terms of the orbital period:
Find the constant of proportionality:
Compare with the exact formula given by Kepler's third law:
The exact constant of proportionality has value:
Compare with the different values from the orbital data directly:
Text
Wolfram Research (2015), FindFormula, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindFormula.html (updated 2017).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2015. "FindFormula." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2017. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindFormula.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2015). FindFormula. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindFormula.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_findformula, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FindFormula}", year="2017", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindFormula.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_findformula, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FindFormula}, year={2017}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FindFormula.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}