

Greater 
Details
- Greater is also known as strong inequality or strict inequality.
- Greater gives True or False when its arguments are real numbers.
- Greater does some simplification when its arguments are not numbers.
- For exact numeric quantities, Greater internally uses numerical approximations to establish numerical ordering. This process can be affected by the setting of the global variable $MaxExtraPrecision.
Examples
open all close allScope (9)
Numeric Inequalities (7)
Inequalities are defined only for real numbers:
Approximate numbers that differ in at most their last eight binary digits are considered equal:
Compare an exact numeric expression and an approximate number:
Compare two exact numeric expressions; a numeric test may suffice to prove inequality:
Proving this inequality requires symbolic methods:
Symbolic and numeric methods used by Greater are insufficient to disprove this inequality:
Use RootReduce to decide the sign of algebraic numbers:
Numeric methods used by Greater do not use sufficient precision to prove this inequality:
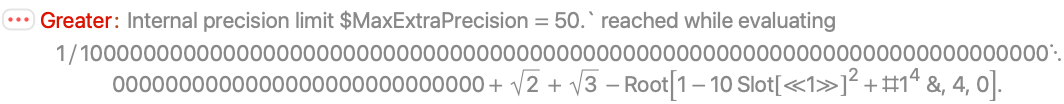
RootReduce proves the inequality using exact methods:
Increasing $MaxExtraPrecision may also prove the inequality:
Symbolic Inequalities (2)
Symbolic inequalities remain unevaluated, since x may not be a real number:
Use Refine to reevaluate the inequality assuming that x is real:
Use Reduce to find an explicit description of the solution set:
Use FindInstance to find a solution instance:
Use Minimize to optimize over the inequality-defined region:
Use Refine to simplify under the inequality defined assumptions:
Properties & Relations (12)
The negation of two-argument Greater is LessEqual:
The negation of three-argument Greater does not simplify automatically:
Use LogicalExpand to express the negation in terms of two-argument LessEqual:
This is not equivalent to three-argument LessEqual:
When Greater cannot decide inequality between numeric expressions it returns unchanged:
FullSimplify uses exact symbolic transformations to disprove the inequality:
Positive[x] is equivalent to ![]() :
:
Use Reduce to solve inequalities:
Use FindInstance to find solution instances:
Use RegionPlot and RegionPlot3D to visualize solution sets of inequalities:
Use Minimize and Maximize to solve optimization problems constrained by inequalities:
Use NMinimize and NMaximize to numerically solve constrained optimization problems:
Integrate a function over the solution set of inequalities:
Use Median, Quantile, and Quartiles to the ![]()
![]() greatest number(s):
greatest number(s):
Possible Issues (3)
Inequalities for machine-precision approximate numbers can be subtle:
The strict inequality is based on extra digits:
Arbitrary-precision approximate numbers do not have this problem:
Thanks to automatic precision tracking, Greater knows to look only at the first 10 digits:
In this case, inequality between machine numbers gives the expected result:
The extra digits in this case are ignored by Greater:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 1988 (1.0) | Updated in 1996 (3.0)
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Greater, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Greater.html (updated 1996).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Greater." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 1996. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Greater.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Greater. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Greater.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_greater, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Greater}", year="1996", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Greater.html}", note=[Accessed: 12-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_greater, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Greater}, year={1996}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Greater.html}, note=[Accessed: 12-March-2026]}