LocalAdaptiveBinarize[image,r]
creates a binary image from image by replacing values above the mean of the range-r neighborhood with 1 and others with 0.
LocalAdaptiveBinarize[image,r,{α,β,γ}]
replaces values above ![]() with 1 and others with 0, where
with 1 and others with 0, where ![]() and
and ![]() are the local mean and standard deviation.
are the local mean and standard deviation.


LocalAdaptiveBinarize
LocalAdaptiveBinarize[image,r]
creates a binary image from image by replacing values above the mean of the range-r neighborhood with 1 and others with 0.
LocalAdaptiveBinarize[image,r,{α,β,γ}]
replaces values above ![]() with 1 and others with 0, where
with 1 and others with 0, where ![]() and
and ![]() are the local mean and standard deviation.
are the local mean and standard deviation.
Details and Options

- Local adaptive binarization determines the binarization thresholds locally and is typically used for segmenting the foreground of an image with nonuniform illumination or background.
- LocalAdaptiveBinarize[image,r] is equivalent to LocalAdaptiveBinarize[image,r,{1,0,0}].
- Using radius r, local mean and standard deviation are computed over
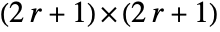 blocks centered on each pixel.
blocks centered on each pixel. - LocalAdaptiveBinarize assumes the index coordinate system for images.
- LocalAdaptiveBinarize works with 2D and 3D images, starting the binarization by converting multichannel and color images into grayscale.
- The following options can be used:
-
Padding "Fixed" what padding scheme to use PerformanceGoal $PerformanceGoal what aspect of performance to optimize
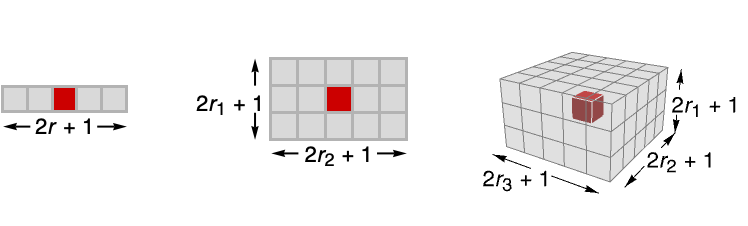
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (1)
Scope (10)
Parameters (7)
Specify a radius parameter of 1 to use 3×3 neighborhoods:
Specify a radius parameter of 10 to use 21×21 neighborhoods:
Segment pixels brighter than the local average around them:
Segment pixels brighter than the fraction 0.9 of the local average:
Segment pixels brighter than the local average plus half the standard deviation:
Segment pixels brighter than the local average minus 0.05:
Specify thresholding coefficients for local average, local standard deviation, and offset:
Options (8)
PerformanceGoal (4)
Use PerformanceGoal->"Quality" to emphasize quality of the result:
Use PerformanceGoal->"Speed" to emphasize speed of computation:
With PerformanceGoal->"Speed", the quality degrades toward the right and bottom:
Using PerformanceGoal->"Quality", computation time increases with respect to the radius:
Applications (3)
Features under uneven illumination are typically not recognized correctly:
TextRecognize fails in this case and returns only a few letters:
Improve the result of text recognition by removing uneven illumination:
Properties & Relations (1)
Related Guides
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), LocalAdaptiveBinarize, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LocalAdaptiveBinarize.html (updated 2016).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "LocalAdaptiveBinarize." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2016. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LocalAdaptiveBinarize.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). LocalAdaptiveBinarize. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LocalAdaptiveBinarize.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_localadaptivebinarize, author="Wolfram Research", title="{LocalAdaptiveBinarize}", year="2016", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LocalAdaptiveBinarize.html}", note=[Accessed: 22-January-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_localadaptivebinarize, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={LocalAdaptiveBinarize}, year={2016}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/LocalAdaptiveBinarize.html}, note=[Accessed: 22-January-2026]}