MardiaKurtosisTest[data]
tests whether data follows a MultinormalDistribution using the Mardia kurtosis test.
MardiaKurtosisTest[data,"property"]
returns the value of "property".


MardiaKurtosisTest
MardiaKurtosisTest[data]
tests whether data follows a MultinormalDistribution using the Mardia kurtosis test.
MardiaKurtosisTest[data,"property"]
returns the value of "property".
Details and Options



- MardiaKurtosisTest performs the Mardia kurtosis goodness-of-fit test with null hypothesis
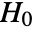 that data was drawn from a MultinormalDistribution and alternative hypothesis
that data was drawn from a MultinormalDistribution and alternative hypothesis 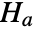 that it was not.
that it was not. - By default, a probability value or
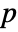 -value is returned.
-value is returned. - A small
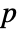 -value suggests that it is unlikely that the data is normally distributed.
-value suggests that it is unlikely that the data is normally distributed. - The data can be univariate {x1,x2,…} or multivariate {{x1,y1,…},{x2,y2,…},…}.
- The Mardia kurtosis test effectively compares a multivariate measure of kurtosis for data to a MultinormalDistribution.
- MardiaKurtosisTest[data,dist,"HypothesisTestData"] returns a HypothesisTestData object htd that can be used to extract additional test results and properties using the form htd["property"].
- MardiaKurtosisTest[data,dist,"property"] can be used to directly give the value of "property".
- PearsonChiSquareTest[data,dist,"property"] can be used to directly give the value of "property".
- Properties related to the reporting of test results include:
-
"DegreesOfFreedom" the degrees of freedom used in a test "PValue" 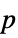 -value
-value"PValueTable" formatted version of "PValue" "ShortTestConclusion" a short description of the conclusion of a test "TestConclusion" a description of the conclusion of a test "TestData" test statistic and 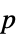 -value
-value"TestDataTable" formatted version of "TestData" "TestStatistic" test statistic "TestStatisticTable" formatted "TestStatistic" - The following properties are independent of which test is being performed.
- Properties related to the data distribution include:
-
"FittedDistribution" fitted distribution of data "FittedDistributionParameters" distribution parameters of data - The following options can be given:
-
Method Automatic the method to use for computing 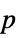 -values
-valuesSignificanceLevel 0.05 cutoff for diagnostics and reporting - For a test for goodness-of-fit, a cutoff
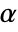 is chosen such that
is chosen such that 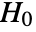 is rejected only if
is rejected only if 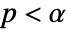 . The value of
. The value of 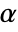 used for the "TestConclusion" and "ShortTestConclusion" properties is controlled by the SignificanceLevel option. By default,
used for the "TestConclusion" and "ShortTestConclusion" properties is controlled by the SignificanceLevel option. By default, 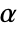 is set to 0.05.
is set to 0.05. - The following methods can be used to compute
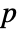 -values:
-values: -
Automatic correct for small samples up to dimension 5 "Asymptotic" use the asymptotic distribution of the test statistic "MonteCarlo" use Monte Carlo simulation - With the setting Method-> "MonteCarlo",
 datasets of the same length as the input
datasets of the same length as the input 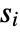 are generated under
are generated under 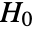 using the fitted distribution. The EmpiricalDistribution from "MonteCarlo" MardiaKurtosisTest[si,"TestStatistic"] is then used to estimate the
using the fitted distribution. The EmpiricalDistribution from "MonteCarlo" MardiaKurtosisTest[si,"TestStatistic"] is then used to estimate the 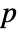 -value.
-value.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (5)
Testing (2)
Perform a Mardia kurtosis test for multivariate normality:
The ![]() -value for the normal data is large compared to the
-value for the normal data is large compared to the ![]() -value for the non-normal data:
-value for the non-normal data:
Create a HypothesisTestData object for repeated property extraction:
Options (4)
Method (3)
Use Monte Carlo-based methods or a computation formula:
Set the number of samples to use for Monte Carlo-based methods:
The Monte Carlo estimate converges to the true ![]() -value with increasing samples:
-value with increasing samples:
Set the random seed used in Monte Carlo-based methods:
The seed affects the state of the generator and has some effect on the resulting ![]() -value:
-value:
Applications (2)
A power curve for the Mardia kurtosis test:
Visualize the approximate power curve:
Estimate the power of the Mardia kurtosis test when the underlying distribution is a MultivariateTDistribution, the test size is 0.05, and the sample size is 27:
Measures of petal and sepal dimensions for three varieties of iris were recorded. A multivariate test of means can be used as a quick check that the measures might be useful in discriminating between two similar species but is only valid if the data follows a multivariate normal distribution:
The multivariate kurtosis of the two species is similar to a multivariate normal distribution:
The multivariate skewness should also be checked to confirm normality:
The data appears normal, so TTest is valid:
Properties & Relations (5)
The multivariate test statistic:
The univariate test statistic:
The multivariate test statistic has an asymptotic NormalDistribution[0,1]:
The asymptotic ![]() -value can be very inaccurate for small samples:
-value can be very inaccurate for small samples:
For comparison, the Monte Carlo ![]() -value is much closer to the small-sample value:
-value is much closer to the small-sample value:
Mardia's kurtosis test can only detect departures from normality in kurtosis:
The data is clearly not normally distributed:
Decisions should be based on MardiaSkewnessTest and MardiaKurtosisTest:
The Mardia kurtosis test works with the values only when the input is a TimeSeries:
Possible Issues (1)
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2010), MardiaKurtosisTest, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MardiaKurtosisTest.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2010. "MardiaKurtosisTest." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MardiaKurtosisTest.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2010). MardiaKurtosisTest. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MardiaKurtosisTest.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_mardiakurtosistest, author="Wolfram Research", title="{MardiaKurtosisTest}", year="2010", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MardiaKurtosisTest.html}", note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_mardiakurtosistest, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={MardiaKurtosisTest}, year={2010}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MardiaKurtosisTest.html}, note=[Accessed: 26-February-2026]}