MoleculeMesh
MoleculeMesh[mol]
returns a BoundaryMeshRegion object representing the Molecule or BioMolecule mol.
MoleculeMesh[mol,type]
returns a mesh of surface type type.
MoleculeMesh[mol,{type,param1val1,…}]
uses the supplied parameters to create the mesh.
Details and Options

- Supported mesh types include
-
"Gaussian" Gaussian surface "VanDerWaals" Van der Waals surface "SolventAccessible" solvent accessible surface "BallAndStick" spheres for atoms and cylinders for bonds - The "VanDerWaals" surface is a union of spheres for each atom using its van der Waals radius.
- A Gaussian surface is defined as an isosurface of the scalar field defined by

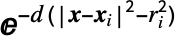 , where xi and ri are the position and radius of the i
, where xi and ri are the position and radius of the i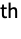 atom, respectively, and d is a prefactor. The "Gaussian" surface has the following parameters and default values:
atom, respectively, and d is a prefactor. The "Gaussian" surface has the following parameters and default values: -
"GaussianPrefactor" 0.9 the parameter d "Isosurface" 1.1 the value of the isosurface - The "SolventAccessible" surface has the following parameters and default values:
-
"ProbeRadius" 1.4 an atom radius that is added to each atom in the molecule - MoleculeMesh has the following options:
-
MaxCellMeasure Automatic max cell measure IncludeWaters False whether to include waters of hydration IncludeHydrogens Automatic whether to include hydrogen atoms - SurfaceArea and Volume will act on a molecule mesh to return the surface are and volume as real numbers, with units of Angstroms2 and Angstroms3, respectively.
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (3)
Create a mesh region showing the atoms and bonds as spheres and tubes:
Show the same molecule with no bonds and atoms represented as spheres with their van der Waals radii:
Use different parameter settings for the "Gaussian" surface:
Combine a Gaussian mesh with a ribbon diagram from BioMoleculePlot3D to show the ribbons in place:
Options (2)
IncludeWaters (1)
Some biomolecules have extra water molecules taken from the crystal structure. These typically have no hydrogens attached. By default, these are not included in a MoleculeMesh output. Use the option IncludeWatersTrue to show the waters:
MaxCellMeasure (1)
Use the option MaxCellMeasure to control the mesh quality:
Neat Examples (2)
Start with two different conformers for a metacyclophane molecule:
View the ball-and-stick mesh regions:
Create Gaussian surfaces for these conformers:
Find the surface area and volume:
Find the isomers of decane with the smallest and largest surface areas:
A greater degree of branching leads to a decrease in the surface area:
Create a scatter plot of the volume versus surface area for these isomers:
Text
Wolfram Research (2025), MoleculeMesh, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MoleculeMesh.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "MoleculeMesh." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MoleculeMesh.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). MoleculeMesh. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/MoleculeMesh.html