QBinomial[n,m,q]
gives the ![]() -binomial coefficient
-binomial coefficient ![]() .
.


QBinomial
QBinomial[n,m,q]
gives the ![]() -binomial coefficient
-binomial coefficient ![]() .
.
Details
- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
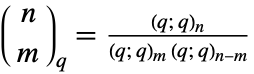 .
.- QBinomial automatically threads over lists.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
Exact evaluation with numbers:
Plot over a subset of the reals:
Plot over a subset of the complexes:
Series expansion at the origin:
Series expansion at Infinity:
Use FunctionExpand to obtain Gaussian polynomials:
Scope (20)
Numerical Evaluation (5)
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate efficiently at high precision:
Compute the elementwise values of an array:
Or compute the matrix QBinomial function using MatrixFunction:
Specific Values (5)
QBinomial for symbolic parameters:
Find the minimum of QBinomial[3,2,q]:
QBinomial threads elementwise over lists:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Visualization (2)
Plot the QBinomial function for various parameters:
Function Properties (4)
![]() has both singularities and discontinuities for
has both singularities and discontinuities for ![]() and for
and for ![]() :
:
![]() is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
QBinomial is neither convex nor concave:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Differentiation (2)
Series Expansions (2)
Find the Taylor expansion using Series:
Generalizations & Extensions (1)
QBinomial can be applied to a power series:
Applications (4)
Explicit combinatorial construction of QBinomial:
![]() -binomial is a generating function for the sequence in a grid-shading problem:
-binomial is a generating function for the sequence in a grid-shading problem:
Elements in the ![]() -Pascal triangle satisfy two recurrence relations:
-Pascal triangle satisfy two recurrence relations:
The number of subspaces in the ![]() -dimensional vector space over
-dimensional vector space over ![]() with prime-power
with prime-power ![]() :
:
Total number of subspaces in three-dimensional vector space over ![]() :
:
Properties & Relations (2)
Use FunctionExpand and FullSimplify to manipulate expressions containing QBinomial:
See Also
Related Guides
Related Links
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), QBinomial, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/QBinomial.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "QBinomial." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/QBinomial.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). QBinomial. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/QBinomial.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_qbinomial, author="Wolfram Research", title="{QBinomial}", year="2008", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/QBinomial.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_qbinomial, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={QBinomial}, year={2008}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/QBinomial.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-March-2026]}