SpatialObservationRegionQ[reg]
tests whether the geometric or geographic region reg can be an observation in spatial statistics.


SpatialObservationRegionQ
SpatialObservationRegionQ[reg]
tests whether the geometric or geographic region reg can be an observation in spatial statistics.
Details

- Spatial observation regions are also known as observation window and observation region.
- The spatial observation region reg is typically used to describe the region in which point data is collected. Observation regions are necessary in order to obtain correct spatial statistics.
- A spatial observation region has to be bounded and full dimensional, but can be of any dimension. It also needs to be parameter free, i.e. ConstantRegionQ.
-
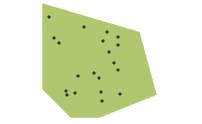

- Geographic regions are typically two-dimensional.
-
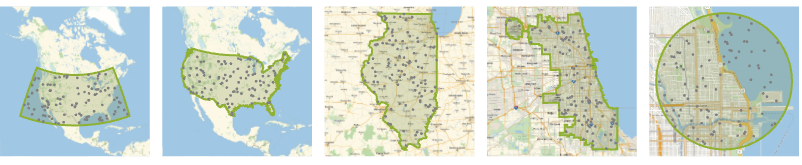
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Properties & Relations (3)
Possible Issues (3)
A network region is not a valid spatial observation region:
This region is not fully dimensional:
A geographical region is bounded if its GeoArea is finite:
It is also bounded and constant in the geometrical sense:
The region dimension and embedding dimension do not agree:
But it is a valid spatial observation region:
For simulation of a point configuration, the region must be parameter free:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), SpatialObservationRegionQ, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SpatialObservationRegionQ.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "SpatialObservationRegionQ." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SpatialObservationRegionQ.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). SpatialObservationRegionQ. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SpatialObservationRegionQ.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_spatialobservationregionq, author="Wolfram Research", title="{SpatialObservationRegionQ}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SpatialObservationRegionQ.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_spatialobservationregionq, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={SpatialObservationRegionQ}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SpatialObservationRegionQ.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}