TransformAnomalies[data,tspec]
transforms anomalies in data using the transformation tspec.
TransformAnomalies[data,dspectspec]
detects the anomalies using the specification dspec.
TransformAnomalies[tab,{col1spec1,…}]
transforms tabular data tab using the specification speci for column coli.


TransformAnomalies
TransformAnomalies[data,tspec]
transforms anomalies in data using the transformation tspec.
TransformAnomalies[data,dspectspec]
detects the anomalies using the specification dspec.
TransformAnomalies[tab,{col1spec1,…}]
transforms tabular data tab using the specification speci for column coli.
Details




- TransformAnomalies is also known as anomaly detection or outlier treatment.
- TransformAnomalies helps maintain data quality by effectively identifying and managing anomalies, ensuring reliable analysis.
- Possible forms of data include:
-
{el1,el2,…} a list of indivudual elements tab tabular data - Possible forms of tabular data tab include:
-
Tabular a tabular object Dataset a dataset object {assoc1,assoc2,…} a list of associations matrix a matrix - Possible transformations tspec for managing the anomalies include:
-
"Clip" limit extreme values to non-anomalies range "Replace" replace anomalies with a calculated value {"Replace",method} replace anomalies using method "Trim" drop the anomalous elements "Flag" replace anomalies with Missing["Anomalous"] tfun use the function tfun to transform the anomalies - Possible "Replace" methods are the same as in TransformMissing:
-
" Mean" the mean value "Median" the median value "Mode" the most frequent value {"Constant", val} a constant value val "RandomElement" randomly selected value {"RandomVariate",dist} value sampled from dist "NearestElement" use the closest non-missing element "NextElement" use the next non-missing element "PreviousElement" use the previous non-missing element "Interpolation" use interpolation {"Interpolation",InterpolationOrderdegree} specify the interpolation order degree - Excluding the anomalies minimizes their influence on analysis. Clipping or replacing minimizes the impact of anomalies while preserving the dataset's structure. Flagging allows keeping all data points for further analysis while highlighting anomalies for review.
- Available methods dspec to detect the anomalies include:
-
"IQR" interquartile range thresholds "ZScore" standard deviations from the mean "ModifiedZScore" robust version using median and MAD {spec,t} specifies the threshold t for anomaly detection {spec,{t1,t2}} specifies the lower and upper thresholds - Additionally, the following specifications are supported:
-
Scaled[f] a fraction f of the smallest and largest elements Scaled[{f1,f2}] separate thresholds for smallest and largest elements dfun a custom function fun - A custom anomaly detector dfun is applied to each element individually and must return a Boolean value.
- When specifying the desired columns, coli can have the following format:
-
n the n 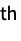 column
column
"name" the column "name" TypeSpecifier[…] columns matching the specified type All all the columns Automatic automatically find columns based on spec (default)
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (16)
Data Types (5)
Detect anomalies in a TabularColumn:
Detect anomalies along matrix columns:
Detect anomalies in a Tabular object:
Detect anomalies in a list of associations across the same key:
Detection Methods (6)
Transformation Methods (5)
Clip the anomalies with the closest valid value:
Replace the anomalies with missing elements:
Apply any TransformMissing specification:
Applications (2)
Take a Tabular object of sales data:
The "Sales" column contains outlier zero values, which are standing in for missing values:
Transform the zero anomalies by removing the relevant rows from the original data:
Transform the zero anomalies by converting them to Missing objects:
Take a Tabular object of weather observations:
It appears the temperature data contains outliers, possibly resulting from entering the data in wrong units. Similarly, the "Pressure" column contains outliers, that is number 99, which is often used in place of missing values. Specify the temperature unit conversion function:
Transform anomalies using the above function for the "Temperature" column and in the "Pressure" column replace the anomaly with the nearest valid value:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2025), TransformAnomalies, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TransformAnomalies.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2025. "TransformAnomalies." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TransformAnomalies.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2025). TransformAnomalies. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TransformAnomalies.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_transformanomalies, author="Wolfram Research", title="{TransformAnomalies}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TransformAnomalies.html}", note=[Accessed: 12-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_transformanomalies, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={TransformAnomalies}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/TransformAnomalies.html}, note=[Accessed: 12-March-2026]}