"SupportVectorMachine" (Machine Learning Method)
- Method for Classify.
- Models class probabilities by finding a hyperplane that separates the training data into two classes using a maximum-margin hyperplane.
Details & Suboptions
- Support vector machines are binary classifiers. A kernel function is used to extract features from the examples. At training time, the method finds the maximum-margin hyperplane that separates classes. The multiclass classification problem is reduced to a set of binary classification problems (using a one-vs.-one or a one-vs.-all strategy). The current implementation uses the LibSVM framework in the back end.
- The option "KernelType" allows you to choose the type of kernel to use. Possible settings for "KernelType" include:
-
"RadialBasisFunction" uses an exponential radial basis function as kernel "Polynomial" uses a polynomial function as kernel "Sigmoid" uses a sigmoidal function as kernel "Linear" uses a linear function as kernel - The kernel "RadialBasisFunction" takes the form:
- The kernel "Polynomial" takes the form:
- The kernel "Sigmoid" takes the form:
- The kernel "Linear" takes the form:
- The following options can be given:
-
"BiasParameter" 1 bias term c in polynomial and sigmoid kernels "GammaScalingParameter" Automatic the parameter 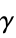 in the preceding kernels
in the preceding kernels"KernelType" "RadialBasisFunction" the kernel to use to map to higher dimensions "MulticlassStrategy" Automatic the strategy to use to obtain a multiclass classifier "PolynomialDegree" 3 the degree of the polynomial d in the polynomial kernel - Possible settings for "MulticlassStrategy" include:
-
"OneVersusOne" train a binary classifier for each pair of classes "OneVersusAll" train one binary classifier for each class - The "GammaScalingParameter" controls the influence of the support vectors. Large values of gamma mean small radius of influence.
- The "PolynomialDegree" option is specific to the polynomial kernel type.
- The "MulticlassStrategy" option is used to generalize binary classifiers to a multiclass ones. The "OneVersusOne" strategy tests each class again each other, while the "OneVersusAll" strategy only test each class against the rest of the training set.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Options (5)
"GammaScalingParameter" (1)
Train a classifier with a specific value for the "GammaScalingParameter" suboption:
The "GammaScalingParameter" controls the influence of the support vectors.
Generate some data and visualize it:
Train two classifiers by changing the "GammaScalingParameter":
Look at how they perform on a test set to see how the radius of influence has changed: