ClusterClassify[data]
generates a ClassifierFunction[…] by partitioning data into clusters of similar elements.
ClusterClassify[data,n]
generates a ClassifierFunction[…] with n clusters.




ClusterClassify
ClusterClassify[data]
generates a ClassifierFunction[…] by partitioning data into clusters of similar elements.
ClusterClassify[data,n]
generates a ClassifierFunction[…] with n clusters.
Details and Options




- ClusterClassify works for a variety of data types, including numerical, textual, and image, as well as dates and times and combinations of these.
- The number of clusters can be specified in the following ways:
-
Automatic find the number of clusters automatically n find exactly n clusters UpTo[n] find at most n clusters - The following options can be given:
-
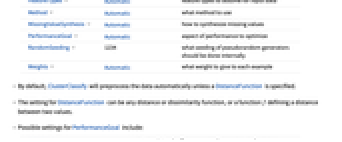
CriterionFunction Automatic criterion for selecting a method DistanceFunction Automatic the distance function to use FeatureExtractor Identity how to extract features from which to learn FeatureNames Automatic feature names to assign for input data FeatureTypes Automatic feature types to assume for input data Method Automatic what method to use MissingValueSynthesis Automatic how to synthesize missing values PerformanceGoal Automatic aspect of performance to optimize RandomSeeding 1234 what seeding of pseudorandom generators should be done internally Weights Automatic what weight to give to each example - By default, ClusterClassify will preprocess the data automatically unless a DistanceFunction is specified.
- The setting for DistanceFunction can be any distance or dissimilarity function, or a function f defining a distance between two values.
- Possible settings for PerformanceGoal include:
-
Automatic automatic tradeoff among speed, accuracy, and memory "Memory" minimize the storage requirements of the classifier "Quality" maximize the accuracy of the classifier "Speed" maximize the speed of the classifier "TrainingSpeed" minimize the time spent producing the classifier - Possible settings for Method include:
-
Automatic automatically select a method "Agglomerate" single linkage clustering algorithm "DBSCAN" density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise "GaussianMixture" variational Gaussian mixture algorithm "JarvisPatrick" Jarvis–Patrick clustering algorithm "KMeans" k-means clustering algorithm "KMedoids" partitioning around medoids "MeanShift" mean-shift clustering algorithm "NeighborhoodContraction" shift data points toward high-density regions "SpanningTree" minimum spanning tree-based clustering algorithm "Spectral" spectral clustering algorithm - The methods "KMeans" and "KMedoids" can only be used when the number of clusters is specified.
- The methods "DBSCAN", "GaussianMixture", "JarvisPatrick", "MeanShift" and "NeighborhoodContraction" can only be used when the number of clusters is Automatic.
- The following plots show results of common methods on toy datasets:
- Possible settings for CriterionFunction include:
-
"StandardDeviation" root-mean-square standard deviation "RSquared" R-squared "Dunn" Dunn index "CalinskiHarabasz" Calinski–Harabasz index "DaviesBouldin" Davies–Bouldin index "Silhouette" Silhouette score Automatic internal index - Possible settings for RandomSeeding include:
-
Automatic automatically reseed every time the function is called Inherited use externally seeded random numbers seed use an explicit integer or strings as a seed - ClusterClassify[…,FeatureExtractor"Minimal"] indicates that the internal preprocessing should be as simple as possible.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Train the ClassifierFunction on some numerical data:
Use the classifier function to classify a new unlabeled example:
Obtain classification probabilities for this example:
Plot the probabilities for the two different classes in the interval {-5,5}:
Train the ClassifierFunction on some colors by requiring the number of classes to be 5:
Use the ClassifierFunction on some unlabeled data:
Gather the elements by their class number:
Train the ClassifierFunction on some strings:
Scope (11)
Use the classifier to assign clusters to a new Boolean True, False vector:
Use the classifier to assign clusters to a Boolean 1, 0 vector:
Use the classifier to cluster new images:
Use the classifier to cluster new strings:
Use the classifier to cluster the data:
Look at the classifier information:
Get a description for the specific method used:
Generate random points in the plane and visualize them:
Classify new random points in the place:
Visualize the resulting clustering:
Classify the same test data using IndeterminateThreshold:
Visualize the resulting clustering including the Indeterminate cluster:
Options (10)
CriterionFunction (1)
Generate some separated data and visualize it:
Construct a classifier function using the Automatic CriterionFunction:
Construct a classifier function using the Calinski–Harabasz index as CriterionFunction:
FeatureExtractor (1)
Create a ClassifierFunction from a list of images and classify new examples:
Create a custom FeatureExtractor to extract features:
FeatureNames (1)
FeatureTypes (1)
Method (2)
Generate some data using uniform distributions:
Use Information to obtain a method description:
Classify the data using k-means:
Generate a large dataset using multinormal distributions and visualize it:
Use ClusterClassify to find clusters by specifying the method to use and look at the AbsoluteTiming:
Look at the resulting clustering:
Use ClusterClassify to find clusters without specifying the method to use and look at the AbsoluteTiming:
MissingValueSynthesis (1)
Generate a large dataset using multinormal distributions and visualize it:
Use ClusterClassify to find clusters:
Get the top cluster probabilities for a point with missing data:
Set the missing value synthesis to replace each missing variable with its estimated most likely value given known values (which is the default behavior):
Replace missing variables with random samples conditioned on known values:
Get the distribution of likely clusters for the point by replacing missing variables repeatedly with the random sampling strategy:
PerformanceGoal (1)
Generate a uniformly distributed dataset and visualize it:
Obtain a classifier from this data, with an emphasis on training speed:
Assign clusters to some randomly generated data and look at the AbsoluteTiming:
Obtain a classifier from this data, with an emphasis on the speed:
Assign clusters to some randomly generated data and look at the AbsoluteTiming compared to the one above:
Visualize the two clusterings for the test data and note how the setting "TrainingSpeed" gives better results:
RandomSeeding (1)
Train several classifiers on random colors:
Compute the classifiers on a new color and observe that the result is always the same:
Train several classifiers on the same colors by using different values of the RandomSeeding option:
Compute the classifiers on ![]() and observe how the classifier differs:
and observe how the classifier differs:
Applications (3)
Train several classifiers on a small, uniformly distributed dataset:
Divide a triangle into segments by using the classifiers on a large number of uniformly distributed random points:
Generate some normally distributed data:
Clusterize the data without specifying the number of classes:
Clusterize the data, specifying the number of classes:
Find dominant colors in an image:
Cluster the data given by the array of pixel values of the image:
Use the classifier to assign clusters to each pixel:
Use the classifier function to find four dominant colors:
Use the classifier to get binary masks for each dominant color:
Tech Notes
History
Introduced in 2016 (10.4) | Updated in 2017 (11.1) ▪ 2017 (11.2) ▪ 2018 (11.3) ▪ 2020 (12.1)
Text
Wolfram Research (2016), ClusterClassify, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ClusterClassify.html (updated 2020).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2016. "ClusterClassify." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2020. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ClusterClassify.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2016). ClusterClassify. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ClusterClassify.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_clusterclassify, author="Wolfram Research", title="{ClusterClassify}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ClusterClassify.html}", note=[Accessed: 12-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_clusterclassify, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={ClusterClassify}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/ClusterClassify.html}, note=[Accessed: 12-March-2026]}