AcousticAbsorbingValue
AcousticAbsorbingValue[pred,vars,pars]
represents a time or frequency domain absorbing boundary condition for PDEs with predicate pred indicating where it applies, with model variables vars and global parameters pars.
AcousticAbsorbingValue[pred,vars,pars,lkeys]
represents a time or frequency domain boundary condition with local parameters specified in pars[lkey].
Details



- AcousticAbsorbingValue specifies a boundary condition for AcousticPDEComponent and is used as part of the modeling equation:
- AcousticAbsorbingValue is typically used to truncate an infinite region to a finite one where the pressure wave is absorbed at the truncation boundary.
- AcousticAbsorbingValue models a time or frequency domain absorption with dependent variable pressure
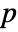 in
in 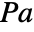 , independent variables
, independent variables 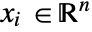 in
in 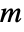 and time variable
and time variable 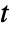 in
in 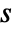 or frequency variable
or frequency variable 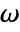 in
in 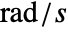 .
. - Time-dependent variables vars are vars={p[t,x1,…,xn],t,{x1,…,xn}}.
- Frequency-dependent variables vars are vars={p[x1,…,xn],ω,{x1,…,xn}}.
- The time domain acoustics model AcousticPDEComponent is based on a wave equation with time variable
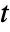 , density
, density 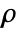 , sound speed
, sound speed 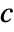 and sound sources
and sound sources 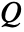 and
and 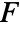 :
: - The frequency domain acoustics model AcousticPDEComponent is based on a Helmholtz equation with angular frequency
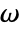 :
: - The time domain absorbing value AcousticAbsorbingValue with sound source absorbing term
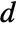 in
in 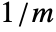 and boundary unit normal
and boundary unit normal 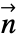 models:
models: - The frequency domain absorbing value AcousticAbsorbingValue models:
- Model parameters pars are specified as for AcousticPDEComponent.
- The dipole source
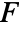 will only be valid within the domain and thus can be excluded from the boundary conditions.
will only be valid within the domain and thus can be excluded from the boundary conditions. - The following model parameters pars can be given:
-
parameter default symbol "MassDensity" 1 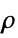 , density of media in
, density of media in 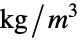
"AcousticSourceDistance" 0 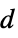 , inverse source distance in
, inverse source distance in 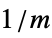
"Material" Automatic 
"SoundSpeed" 1 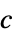 , speed of sound in
, speed of sound in 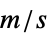
- With different types of incident waves and a distance
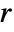 in
in 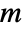 between the wave origin to the boundary
between the wave origin to the boundary 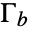 , the absorbing boundary condition term
, the absorbing boundary condition term 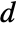 in
in 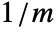 is given by:
is given by: -
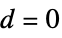
plane wave in 1D, 2D, 3D 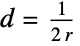
cylindrical wave in 2D, 3D 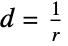
spherical wave in 3D - AcousticAbsorbingValue is most efficient when the incident wave is orthogonal to the absorbing boundary.
- AcousticAbsorbingValue evaluates to a generalized NeumannValue.
- The boundary predicate pred can be specified as in NeumannValue.
- An absorbing boundary can be used with:
-
analysis type applicable Time Domain Yes Frequency Domain Yes Eigenfrequency No - If the AcousticAbsorbingValue depends on parameters
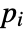 that are specified in the association pars as …,keypi…,pivi,…], the parameters
that are specified in the association pars as …,keypi…,pivi,…], the parameters 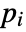 are replaced with
are replaced with 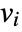 .
. - An alternative to an AcousticAbsorbingValue is a perfectly matched layer (PML) in the time domain or the frequency domain. A perfectly matched layer is preferable when the incident wave is not orthogonal to the absorbing boundary.
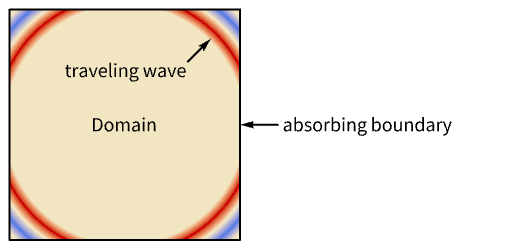
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (4)
Define model variables vars for a transient acoustic pressure field with model parameters pars and a specific boundary condition parameter:
Define model variables vars for a transient acoustic pressure field with model parameters pars and multiple specific parameters boundary conditions:
Define model variables vars for a transient acoustic pressure field with model parameters pars:
Set up initial conditions ics of a right-going plane wave ![]() :
:
Set up the equation with an acoustic absorbing boundary at the right end for a plane wave:
Define model variables vars for a frequency domain acoustic pressure field with model parameters pars:
Set up the equation with a radiation boundary at the left end and an acoustic absorbing boundary at the right end:
Visualize the solution in the frequency domain at various frequencies ![]() :
:
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), AcousticAbsorbingValue, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AcousticAbsorbingValue.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "AcousticAbsorbingValue." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AcousticAbsorbingValue.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). AcousticAbsorbingValue. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/AcousticAbsorbingValue.html