DiscreteHadamardTransform[list]
gives the discrete Hadamard transform of list.


DiscreteHadamardTransform
DiscreteHadamardTransform[list]
gives the discrete Hadamard transform of list.
Details and Options

- DiscreteHadamardTransform is also known as the Walsh transform and Walsh–Hadamard transform.
- The discrete Hadamard transform
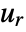 of a list
of a list 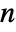 of length
of length 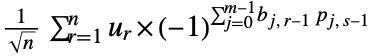 is by default defined to be
is by default defined to be 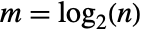 , where
, where 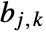 ,
, 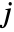 is the
is the 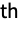
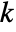 bit in the binary representation of the integer
bit in the binary representation of the integer 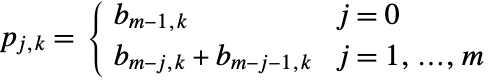 , and
, and 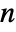 .
. - DiscreteHadamardTransform returns a list whose length is a power of 2. If the length of the input list is not a power of 2, it is zero padded to a length that is the smallest power of 2 greater than
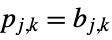 .
. - DiscreteHadamardTransform takes a Method option, which specifies the sequency ordering (number of zero crossings in the Hadamard basis sequences) of the transform. Possible settings include:
-
"BitComplement" 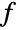
"GrayCode" Gray code reordering of "BitComplement" "Sequency" sequency increases with row and column index (default) - The bit complement ordering is also known as the Sylvester ordering.
- The sequency ordering is also known as the Walsh ordering.
- The Gray code ordering is also known as the dyadic ordering or Paley ordering.
- The forward and inverse Hadamard transforms are identical. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (1)
Options (1)
Applications (1)
Properties & Relations (3)
The discrete Hadamard transform is its own inverse (an involution):
DiscreteHadamardTransform automatically pads with zeros to the nearest power of 2:
Define a function for generating a bit-reversal permutation:
Define a function for generating a Gray code permutation:
Generate random data and take its discrete Hadamard transform for different sequency orderings:
The Hadamard transform with Gray code ordering is equivalent to applying the Gray code permutation to the Hadamard transform with bit-complement sequency ordering:
The Hadamard transform with sequency ordering is equivalent to applying the bit-reversal permutation to the Hadamard transform with Gray code ordering:
The Hadamard transform with sequency ordering is equivalent to successively applying the bit-reversal permutation and Gray code permutation to the Hadamard transform with bit-complement sequency ordering:
See Also
Related Guides
Related Links
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), DiscreteHadamardTransform, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteHadamardTransform.html (updated 2024).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "DiscreteHadamardTransform." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2024. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteHadamardTransform.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). DiscreteHadamardTransform. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteHadamardTransform.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_discretehadamardtransform, author="Wolfram Research", title="{DiscreteHadamardTransform}", year="2024", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteHadamardTransform.html}", note=[Accessed: 22-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_discretehadamardtransform, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={DiscreteHadamardTransform}, year={2024}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiscreteHadamardTransform.html}, note=[Accessed: 22-February-2026]}