FaceRecognize[{example1name1,example2name2,…}]
generates a ClassifierFunction[…] based on the face examples and names given.
FaceRecognize[{example1,example2,…}{name1,name2,…}]
also generates a ClassifierFunction[…] based on the examples and names given.
FaceRecognize[name1{example11,…},name2{example21,…},…]
uses an association of names with their examples.
FaceRecognize[training,image]
attempts to find faces present in an image and classify them with the given training set.
FaceRecognize[training,image,prop]
returns the specified property prop.


FaceRecognize
FaceRecognize[{example1name1,example2name2,…}]
generates a ClassifierFunction[…] based on the face examples and names given.
FaceRecognize[{example1,example2,…}{name1,name2,…}]
also generates a ClassifierFunction[…] based on the examples and names given.
FaceRecognize[name1{example11,…},name2{example21,…},…]
uses an association of names with their examples.
FaceRecognize[training,image]
attempts to find faces present in an image and classify them with the given training set.
FaceRecognize[training,image,prop]
returns the specified property prop.
Details and Options

- FaceRecognize can be trained to be used for recognizing occurrences of people's faces in images.
- FaceRecognize[training,{image1,image2,…}], returns recognized faces in all imagei.
- By default, FaceRecognize gives a list of names associated with faces it recognizes.
- Possible settings for property prop are:
-
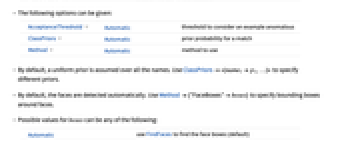
"BoundingBox" bounding Rectangle of the face "Image" a crop of image corresponding to the face "Name" name associated to a face "Position" the position of each face given as {x,y} "Probability" probability for a specific match "RarerProbability" probability to generate a sample with lower PDF than faces in image {prop1,prop2,…} a list of property specifications - The following options can be given:
-
AcceptanceThreshold Automatic threshold to consider an example anomalous ClassPriors Automatic prior probability for a match Method Automatic method to use - By default, a uniform prior is assumed over all the names. Use ClassPriors<|name1p1,…|> to specify different priors.
- By default, the faces are detected automatically. Use Method{"FaceBoxes"boxes} to specify bounding boxes around faces.
- Possible values for boxes can be any of the following:
-
Automatic use FindFaces to find the face boxes (default) Full the whole image is assumed to be one face {bbox1,…} a list of bounding boxes for faces - FaceRecognize uses machine learning. Its methods, training sets and biases included therein may change and yield varied results in different versions of the Wolfram Language.
- FaceRecognize may download resources that will be stored in your local object store at $LocalBase, and that can be listed using LocalObjects[] and removed using ResourceRemove.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Recognize if a given person is present in an image:
Create a ClassifierFunction from a set of images:
Apply the classifier to a face:
If a face is not among the training examples, Missing is returned:
Scope (6)
Create a ClassifierFunction that can recognize faces:
If the face is not recognized, Missing is returned:
Provide multiple references for the same person:
Group the references in an Association:
Return all supported properties:
Options (3)
AcceptanceThreshold (1)
Specify AcceptanceThreshold to control how many faces are recognized:
Use a lower value to recognize faces far from the training distribution:
Using AcceptanceThreshold0 always returns the nearest class to the test image:
ClassPriors (1)
By default, FaceRecognize assumes uniform probability among the classes:
Applications (4)
Verify whether two faces belong to the same person:
Create a function that detects whether an image contains a specified person:
Test whether a person appears in an image:
FaceRecognize can be used to find the face nearest to the test image:
Build a face-search function that returns the position of images that contain a specific person:
Possible Issues (2)
Training is still performed with images that may not be faces:
Testing can also be done with images that may not be faces:
FaceRecognize expects face crops for all training face samples:
See Also
FindFaces Classify FaceAlign FacialFeatures ImageIdentify ImageContents TextRecognize ImageKeypoints ImageAlign
Classifiers: NotablePerson
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), FaceRecognize, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FaceRecognize.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "FaceRecognize." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FaceRecognize.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). FaceRecognize. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FaceRecognize.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_facerecognize, author="Wolfram Research", title="{FaceRecognize}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FaceRecognize.html}", note=[Accessed: 01-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_facerecognize, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={FaceRecognize}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/FaceRecognize.html}, note=[Accessed: 01-March-2026]}