IndependenceTest[v1,v2]
tests whether the vectors v1 and v2 are independent.
IndependenceTest[m1,m2]
tests whether the matrices m1 and m2 are independent.
IndependenceTest[…,"property"]
returns the value of "property".


IndependenceTest
IndependenceTest[v1,v2]
tests whether the vectors v1 and v2 are independent.
IndependenceTest[m1,m2]
tests whether the matrices m1 and m2 are independent.
IndependenceTest[…,"property"]
returns the value of "property".
Details and Options


- IndependenceTest performs a hypothesis test on v1 and v2 with null hypothesis
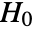 that the vectors are independent, and alternative hypothesis
that the vectors are independent, and alternative hypothesis 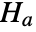 that they are not.
that they are not. - By default, a probability value or
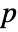 -value is returned.
-value is returned. - A small
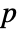 -value suggests that it is unlikely that
-value suggests that it is unlikely that 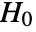 is true.
is true. - The arguments v1 and v2 can be any real-valued vectors or matrices of equal length.
- IndependenceTest[v1,v2] will choose the most powerful test that applies to v1 and v2.
- IndependenceTest[v1,v2,All] will choose all tests that apply to v1 and v2.
- IndependenceTest[v1,v2,"test"] reports the
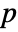 -value according to "test".
-value according to "test". - Some of the available tests assume normality for the vi. Some tests are restricted to vectors. Most tests are restricted to tests of monotonic or linear independence.
- The following tests can be used:
-
"BlomqvistBeta" monotonic based on Blomqvist's 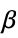
"GoodmanKruskalGamma" monotonic, vector based on the 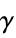 -coefficient
-coefficient"HoeffdingD" vector based on Hoeffding's 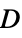
"KendallTau" monotonic based on Kendall's 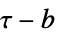
"PearsonCorrelation" linear, normality, vector based on Pearson product-moment 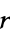
"PillaiTrace" normality, linear based on Pillai's trace "SpearmanRank" monotonic based on Spearman's 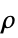
"WilksW" normality, linear based on Wilks' 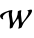
- IndependenceTest[v1,v2,"HypothesisTestData"] returns a HypothesisTestData object htd that can be used to extract additional test results and properties using the form htd["property"].
- IndependenceTest[v1,v2,"property"] can be used to directly give the value of "property".
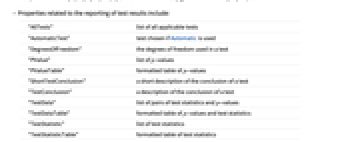
- Properties related to the reporting of test results include:
-
"AllTests" list of all applicable tests "AutomaticTest" test chosen if Automatic is used "DegreesOfFreedom" the degrees of freedom used in a test "PValue" list of 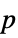 -values
-values"PValueTable" formatted table of 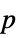 -values
-values"ShortTestConclusion" a short description of the conclusion of a test "TestConclusion" a description of the conclusion of a test "TestData" list of pairs of test statistics and 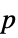 -values
-values"TestDataTable" formatted table of 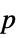 -values and test statistics
-values and test statistics"TestStatistic" list of test statistics "TestStatisticTable" formatted table of test statistics - The following options can be used:
-
AlternativeHypothesis "Unequal" the inequality for the alternative hypothesis MaxIterations Automatic max iterations for multivariate nonparametric tests Method Automatic the method to use for computing 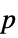 -values
-valuesSignificanceLevel 0.05 cutoff for diagnostics and reporting VerifyTestAssumptions Automatic what assumptions to verify - For tests of independence, a cutoff
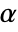 is chosen such that
is chosen such that 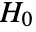 is rejected only if
is rejected only if 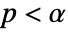 . The value of
. The value of 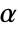 used for the "TestConclusion" and "ShortTestConclusion" properties is controlled by the SignificanceLevel option. This value
used for the "TestConclusion" and "ShortTestConclusion" properties is controlled by the SignificanceLevel option. This value 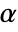 is also used in diagnostic tests of normality. By default,
is also used in diagnostic tests of normality. By default, 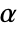 is set to 0.05.
is set to 0.05. - Named settings for VerifyTestAssumptions in IndependenceTest include:
-
"Normality" verify that all data is normally distributed
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (12)
Testing (8)
Test whether two vectors are independent:
The ![]() -values are typically large when the vectors are independent:
-values are typically large when the vectors are independent:
The ![]() -values are typically small when there are dependencies:
-values are typically small when there are dependencies:
Test whether two matrices are independent:
The ![]() -values are typically small for dependent matrices:
-values are typically small for dependent matrices:
The ![]() -values are typically large when matrices are independent:
-values are typically large when matrices are independent:
Using Automatic applies the most powerful appropriate test for linear independence:
The property "AutomaticTest" can be used to determine which test was chosen:
Perform a particular test for independence:
Any number of tests can be performed simultaneously:
Perform all tests appropriate to the data simultaneously:
Use the property "AllTests" to identify which tests were used:
Create a HypothesisTestData object for repeated property extraction:
The properties available for extraction:
Extract some properties from the HypothesisTestData object:
The ![]() -value and test statistic from the "PearsonCorrelation" test:
-value and test statistic from the "PearsonCorrelation" test:
Reporting (4)
Tabulate the results from a selection of tests:
A full table of all appropriate test results:
A table of selected test results:
Retrieve the entries from a test table for customized reporting:
The ![]() -values are above 0.05, so there is not enough evidence to reject
-values are above 0.05, so there is not enough evidence to reject ![]() at that level:
at that level:
Tabulate ![]() -values for a test or group of tests:
-values for a test or group of tests:
A table of ![]() -values from all appropriate tests:
-values from all appropriate tests:
A table of ![]() -values from a subset of tests:
-values from a subset of tests:
Report the test statistic from a test or group of tests:
Options (15)
AlternativeHypothesis (3)
MaxIterations (1)
Method (4)
SignificanceLevel (3)
Set the significance level for diagnostic tests:
By default, 0.05 is used. The message shows 0.025 because two tests were performed:
Setting the significance level may alter which test is automatically chosen:
A nonparametric test would have been chosen by default:
The significance level is also used for "TestConclusion" and "ShortTestConclusion":
VerifyTestAssumptions (4)
By default, normality is tested when appropriate:
Diagnostics can be controlled as a group using All or None:
Diagnostics can be controlled independently:
Explicitly set the diagnostic result:
It is often useful to bypass diagnostic tests for simulation purposes:
The assumptions of the test hold by design, so a great deal of time can be saved:
Properties & Relations (4)
The test chosen depends on normality assumptions and the dimensionality of the data:
Comparison of normally distributed vectors:
The second vector is not from a normal distribution:
Matrix comparison of normally distributed data:
Matrix comparison of data that is not normally distributed:
To test particular values of correlation or rank correlation, use CorrelationTest:
HoeffdingDTest should be used if nonlinear dependency is expected:
The data is clearly dependent:
IndependenceTest does not detect this by default:
Measures of monotone dependence are selected by default:
HoeffdingD is sensitive to many types of dependence:
IndependenceTest works with the values only when the input is a TimeSeries:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), IndependenceTest, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/IndependenceTest.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "IndependenceTest." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/IndependenceTest.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). IndependenceTest. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/IndependenceTest.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_independencetest, author="Wolfram Research", title="{IndependenceTest}", year="2012", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/IndependenceTest.html}", note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_independencetest, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={IndependenceTest}, year={2012}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/IndependenceTest.html}, note=[Accessed: 06-March-2026]}