SpatialRandomnessTest[pdata]
tests whether the point collection pdata is distributed uniformly over the observation region.
SpatialRandomnessTest[pdata,"property"]
returns the value of "property".


SpatialRandomnessTest
SpatialRandomnessTest[pdata]
tests whether the point collection pdata is distributed uniformly over the observation region.
SpatialRandomnessTest[pdata,"property"]
returns the value of "property".
Details and Options



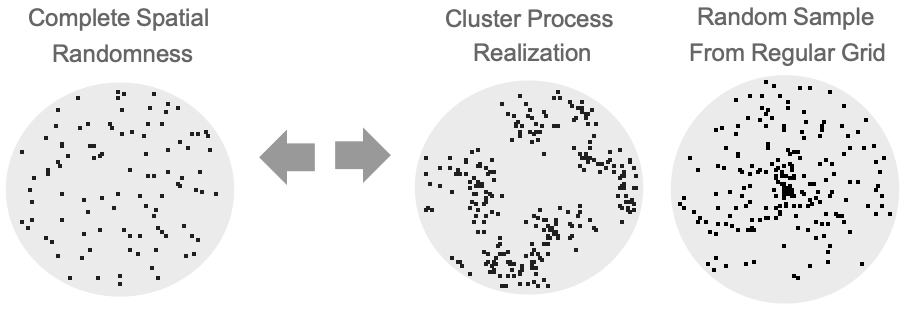
- SpatialRandomnessTest performs a goodness-of-fit hypothesis test with null hypothesis
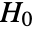 that pdata was drawn from a PoissonPointProcess and alternative hypothesis
that pdata was drawn from a PoissonPointProcess and alternative hypothesis 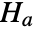 that it was not.
that it was not. -
- By default, a probability value or
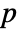 -value is returned.
-value is returned. - A small
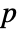 -value suggests that it is unlikely that pdata comes from a PoissonPointProcess.
-value suggests that it is unlikely that pdata comes from a PoissonPointProcess. - The point data pdata can have the following forms:
-
{p1,p2,…} points pi GeoPosition[…],GeoPositionXYZ[…],… geographic points SpatialPointData[…] spatial point collection {pts,reg} point collection pts and observation region reg - If the observation region reg is not given, a region is automatically computed using RipleyRassonRegion.
- SpatialRandomnessTest[pdata,"test"] will report the
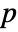 -value according to "test".
-value according to "test". - SpatialRandomnessTest[pdata,All] will choose all tests.
- Under the null hypothesis
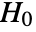 , the points in pdata were drawn from a PoissonPointProcess[λ]. This means they should be uniformly distributed over the given observation region reg. By binning the points, the standard bin count residual
, the points in pdata were drawn from a PoissonPointProcess[λ]. This means they should be uniformly distributed over the given observation region reg. By binning the points, the standard bin count residual 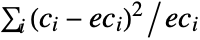 , where
, where 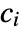 and
and 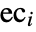 are the count and expected count in bin i, respectively, should be approximately chi-square distributed, and the count
are the count and expected count in bin i, respectively, should be approximately chi-square distributed, and the count 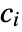 should be multinomially distributed.
should be multinomially distributed. - The following tests can be used:
-
"BesagL" based on BesagL, which is expected to be a straight line as a function of radius, slower and higher statistical power "ChiSquare" based on binning, where standard bin count residuals are expected to be chi-square distributed, fast and approximate "ModifiedChiSquare" based on binning, where counts are expected to be multinomially distributed, exact for small samples, using "ChiSquare" for large data - SpatialRandomnessTest[pdata,"HypothesisTestData"] returns a HypothesisTestData object htd that can be used to extract additional test results and properties using the form htd["property"].
- SpatialRandomnessTest[pdata,"property"] can be used to directly give the value of "property".
- Properties related to the reporting of test results include:
-
"AllTests" list of all applicable tests "AutomaticTest" test chosen if Automatic is used "PValue" list of 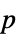 -values
-values"PValueTable" formatted table of 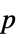 -values
-values"ShortTestConclusion" a short description of the conclusion of a test "TestConclusion" a description of the conclusion of a test "TestData" list of pairs of test statistics and 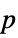 -values
-values"TestDataTable" formatted table of 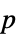 -values and test statistics
-values and test statistics"TestStatistic" list of test statistics "TestStatisticTable" formatted table of test statistics - The following options can be used:
-
SignificanceLevel 0.05 cutoff for diagnostics and reporting
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (10)
Testing (7)
The ![]() -values are typically large when points are uniformly distributed:
-values are typically large when points are uniformly distributed:
The ![]() -values are typically small when there is spatial heterogeneity:
-values are typically small when there is spatial heterogeneity:
Perform a particular test for spatial randomness:
Extract a property for a specific test:
Using Automatic applies the "AutomaticTest" option:
The property "AutomaticTest" can be used to determine which test was chosen:
Perform all tests appropriate to the data simultaneously:
Use the property "AllTests" to identify which tests were used:
Create a HypothesisTestData object for repeated property extraction:
The properties available for extraction:
Extract some properties from the HypothesisTestData object:
The ![]() -value and test statistic from the "ChiSquare" test:
-value and test statistic from the "ChiSquare" test:
Reporting (3)
Tabulate the results from a selection of tests:
A full table of all appropriate test results:
A table of selected test results:
Retrieve the entries from a test table for customized reporting:
The ![]() -values are above 0.05, so there is not enough evidence to reject
-values are above 0.05, so there is not enough evidence to reject ![]() at that level:
at that level:
The significance level is used for "TestConclusion" and "ShortTestConclusion":
Options (1)
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), SpatialRandomnessTest, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SpatialRandomnessTest.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "SpatialRandomnessTest." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SpatialRandomnessTest.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). SpatialRandomnessTest. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SpatialRandomnessTest.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_spatialrandomnesstest, author="Wolfram Research", title="{SpatialRandomnessTest}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SpatialRandomnessTest.html}", note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_spatialrandomnesstest, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={SpatialRandomnessTest}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/SpatialRandomnessTest.html}, note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}