

DiagonalizableMatrixQ
Details and Options
- A matrix m is diagonalizable if it is similar to a diagonal matrix. That is, if there is a nonsingular matrix
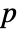 such that
such that 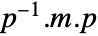 is diagonal.
is diagonal. - DiagonalizableMatrixQ works for symbolic as well as numerical matrices.
- For approximate matrices, the option Tolerance->t can be used to indicate that the determinant of eigenvectors v of the matrix m satisfying Abs[Det[v]]≤t is taken to be zero, which means that the eigenvectors v are linearly dependent and the matrix m is not diagonalizable.
- The option Tolerance has Automatic as its default value.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (9)
Basic Uses (5)
Test if a real machine-precision matrix is diagonalizable:
The diagonal elements of the obtained matrix are the eigenvalues of ![]() :
:
Test if a complex matrix is diagonalizable:
Test if an exact matrix is diagonalizable:
Make the matrix diagonalizable:
Use DiagonalizableMatrixQ with an arbitrary-precision matrix:
A random square matrix is typically diagonalizable:
Use DiagonalizableMatrixQ with a symbolic matrix:
Special Matrices (4)
Use DiagonalizableMatrixQ with sparse matrices:
Use DiagonalizableMatrixQ with structured matrices:
Use with a QuantityArray structured matrix:
The identity matrix is diagonalizable:
HilbertMatrix is diagonalizable:
Options (1)
Tolerance (1)
Generate a real-valued non-diagonalizable Jordan block matrix with some random perturbation of order ![]() :
:
But the eigenvectors v are numerically linearly dependent:
Adjust the option Tolerance so that the linear dependence of the eigenvectors is detected:
Applications (6)
If a matrix ![]() is diagonalizable, it can be decomposed as
is diagonalizable, it can be decomposed as ![]() , where
, where ![]() is nonsingular and
is nonsingular and ![]() is diagonal. This can be used to compute a matrix function by using its power series representation
is diagonal. This can be used to compute a matrix function by using its power series representation ![]() as
as ![]() , and
, and ![]() can be computed by simply applying
can be computed by simply applying ![]() to each of the diagonal elements. Use this method to compute several different matrix functions:
to each of the diagonal elements. Use this method to compute several different matrix functions:
The ![]() matrix has the eigenvectors as columns, and the diagonal entries are the eigenvalues:
matrix has the eigenvectors as columns, and the diagonal entries are the eigenvalues:
Compute ![]() and confirm using MatrixPower:
and confirm using MatrixPower:
Compute ![]() and confirm using MatrixExp:
and confirm using MatrixExp:
Compute ![]() and confirm using MatrixLog:
and confirm using MatrixLog:
Compute ![]() and confirm using MatrixFunction:
and confirm using MatrixFunction:
Solve the system of ODEs ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() . First, construct the coefficient matrix
. First, construct the coefficient matrix ![]() for the right-hand side:
for the right-hand side:
The coefficient matrix is diagonalizable, so computing the matrix exponential will be straightforward:
Find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors:
Construct a diagonal matrix whose entries are the exponential of ![]() :
:
Construct the matrix whose columns are the corresponding eigenvectors:
The general solution is ![]() , for three arbitrary starting values:
, for three arbitrary starting values:
Verify the solution using DSolveValue:
Use the fact that the recurrence relation for Fibonacci, ![]() , can be written in matrix form as
, can be written in matrix form as ![]() to derive a formula for the pair
to derive a formula for the pair ![]() . The solution to the recurrence relation is
. The solution to the recurrence relation is ![]() , where
, where ![]() :
:
Thus, the matrix power can be computed simply using EigenvalueDecomposition[m]:
Confirm the result using Fibonacci:
Normal matrices are the most general kind of matrix that can be unitarily diagonalized as ![]() with
with ![]() diagonal and
diagonal and ![]() unitary. All Hermitian matrices
unitary. All Hermitian matrices ![]() are normal because both sides of the equality are simply
are normal because both sides of the equality are simply ![]() :
:
Similarly, all antihermitian matrices are normal because both sides of the equality are simply ![]() :
:
Unitary matrices are normal, as substituting in the definition ![]() gives an identity matrix on both sides:
gives an identity matrix on both sides:
Show that the following matrix is normal, then diagonalize it:
Confirm using NormalMatrixQ:
A normal matrix like ![]() can be unitarily diagonalized using EigenvalueDecomposition:
can be unitarily diagonalized using EigenvalueDecomposition:
The entries on the diagonal can be arbitrary complex numbers:
While this is a diagonalization, it is not unitary:
The columns of ![]() are orthogonal, as they must be, but they are not normalized:
are orthogonal, as they must be, but they are not normalized:
Normalizing the columns of ![]() gives a unitary matrix:
gives a unitary matrix:
Confirm the unitary diagonalization ![]() :
:
In quantum mechanics, the energy operator is called the Hamiltonian ![]() , and a state with energy
, and a state with energy ![]() evolves according to the Schrödinger equation
evolves according to the Schrödinger equation ![]() . An important assumption is that any state can be written as a sum of eigenstates. Show that this is the case for Hamiltonian for a spin-1 particle in constant magnetic field in the
. An important assumption is that any state can be written as a sum of eigenstates. Show that this is the case for Hamiltonian for a spin-1 particle in constant magnetic field in the ![]() direction:
direction:
The matrix is diagonalizable, so its eigenvectors must form a basis for ![]() :
:
Computing the eigensystem, the energy levels are ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Confirm that the eigenvectors are linearly independent and thus a basis:
Decompose an arbitrary state as a sum of the eigenvectors:
Many matrix distributions produce matrices that are guaranteed to be diagonalizable, including CircularRealMatrixDistribution:
CircularSymplecticMatrixDistribution:
Properties & Relations (9)
A diagonalizable matrix ![]() can be factored as
can be factored as ![]() with
with ![]() diagonal using an eigendecomposition:
diagonal using an eigendecomposition:
Use EigenvalueDecomposition to find the similarity and diagonal matrices:
A matrix is diagonalizable if and only if it has a complete set of eigenvectors:
Although it has repeated eigenvalues, ![]() has three linearly independent eigenvectors:
has three linearly independent eigenvectors:
Despite having the same eigenvalues as ![]() , the matrix
, the matrix ![]() is not diagonalizable:
is not diagonalizable:
It only has two independent eigenvectors, as indicated by the zero vector returned by Eigensystem:
Any matrix with no repeated eigenvalues is diagonalizable:
Any real symmetric matrix is diagonalizable:
Any real antisymmetric matrix is diagonalizable:
As is any antihermitian matrix:
Any real orthogonal matrix is diagonalizable:
Any normal matrix is diagonalizable:
A matrix m is diagonalizable if and only if the ![]() matrix of JordanDecomposition[m] is diagonal:
matrix of JordanDecomposition[m] is diagonal:
An ![]() ×
×![]() matrix
matrix ![]() is nilpotent if
is nilpotent if ![]() for some
for some ![]() :
:
Consider a non-diagonalizable matrix ![]() :
:
Use JordanDecomposition to write ![]() as
as ![]() with
with ![]() diagonalizable and
diagonalizable and ![]() nilpotent:
nilpotent:
Tech Notes
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), DiagonalizableMatrixQ, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiagonalizableMatrixQ.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "DiagonalizableMatrixQ." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiagonalizableMatrixQ.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). DiagonalizableMatrixQ. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiagonalizableMatrixQ.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_diagonalizablematrixq, author="Wolfram Research", title="{DiagonalizableMatrixQ}", year="2014", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiagonalizableMatrixQ.html}", note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_diagonalizablematrixq, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={DiagonalizableMatrixQ}, year={2014}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/DiagonalizableMatrixQ.html}, note=[Accessed: 27-February-2026]}