



Fibonacci
Details

- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
- The
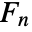 satisfy the recurrence relation
satisfy the recurrence relation 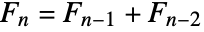 with
with 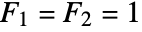 .
. - For any complex value of n, the
 are given by the general formula
are given by the general formula 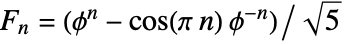 , where
, where 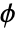 is the golden ratio.
is the golden ratio. - The Fibonacci polynomial
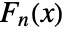 is the coefficient of
is the coefficient of 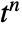 in the expansion of
in the expansion of 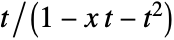 .
. - The Fibonacci polynomials satisfy the recurrence relation
 .
. - FullSimplify and FunctionExpand include transformation rules for combinations of Fibonacci numbers with symbolic arguments when the arguments are specified to be integers using n∈Integers.
- Fibonacci can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- Fibonacci automatically threads over lists.
- Fibonacci can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (6)
Plot over a subset of the reals:
Plot over a subset of the complexes:
Series expansion at the origin:
Series expansion at Infinity:
Scope (43)
Numerical Evaluation (6)
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate efficiently at high precision:
Compute worst-case guaranteed intervals using Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Or compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Compute the elementwise values of an array:
Or compute the matrix Fibonacci function using MatrixFunction:
Specific Values (6)
Visualization (5)
Function Properties (14)
Fibonacci is defined for all real values:
Approximate function range of Fibonacci:
Fibonacci polynomial of an even order is odd:
Fibonacci polynomial of an odd order is even:
Fibonacci has the mirror property ![]() :
:
Fibonacci threads elementwise over lists:
Fibonacci is an analytic function of x:
Fibonacci is neither non-decreasing nor non-increasingfor odd values:
Fibonacci is non-decreasing for even values:
Fibonacci is not injective for odd values:
Fibonacci is not surjective for odd values:
Fibonacci is non-negative for odd values:
Fibonacci has no singularities or discontinuities:
Fibonacci is convex for odd values:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Differentiation (3)
Integration (3)
Series Expansions (4)
Find the Taylor expansion using Series:
Plots of the first three approximations around ![]() :
:
General term in the series expansion using SeriesCoefficient:
Find the series expansion at Infinity:
Function Identities and Simplifications (2)
Applications (13)
Solve the Fibonacci recurrence equation:
Solve another Fibonacci recurrence equation:
Find ratios of successive Fibonacci numbers:
Compare with continued fractions:
Convergence to the golden ratio:
Fibonacci substitution system:
Calculate the number of ways to write an integer as a sum of Fibonacci numbers ![]() :
:
Plot the counts for the first hundred integers:
Lamé's theorem bounds the number of steps of the Euclidean algorithm for calculating ![]() :
:
Plot the maximal number of steps:
Find the first Fibonacci number above 1000000:
Plot the discrete inverse of Fibonacci numbers:
Plot of the absolute value of Fibonacci over the complex plane:
Find the number of factors of Fibonacci polynomials:
This is a particular case of a more general identity ![]() :
:
The sequence of ![]() is periodic with respect to
is periodic with respect to ![]() for a fixed natural number
for a fixed natural number ![]() :
:
Build Zeckendorf's representation of a positive integer [MathWorld]:
Define Fibonacci multiplication for positive integers:
Properties & Relations (15)
Fibonacci Numbers (13)
Expand in terms of elementary functions:
Explicit recursive definition:
Explicit state‐space recursive definition:
Closed‐form solution using MatrixPower:
Simplify expressions involving Fibonacci numbers:
Fibonacci numbers as coefficients:
Express a fractional Fibonacci number as an algebraic number:
Fibonacci can be represented as a DifferenceRoot:
General term in the series expansion of Fibonacci:
The generating function for Fibonacci:
FindSequenceFunction can recognize the Fibonacci sequence:
The exponential generating function for Fibonacci:
Possible Issues (3)
Neat Examples (8)
Fibonacci modulo n [more info]:
Count the number of 1, 2, ..., 9, 0 digits in the 1,000,000![]() Fibonacci number:
Fibonacci number:
Contours of vanishing real and imaginary parts of Fibonacci:
LogPlot of positive and negative Fibonacci numbers:
While the Fibonacci numbers are nondecreasing for non-negative arguments, the Fibonacci function possesses a single local minimum:
Since the generating function is rational, these sums come out as rational numbers:
See Also
GoldenRatio LucasL RSolve LinearRecurrence RecurrenceTable DifferenceRoot GoldenAngle
Function Repository: InverseFibonacci BinetFibonacci ZeckendorfRepresentation FibonacciEncode
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 1996 (3.0) | Updated in 1999 (4.0) ▪ 2000 (4.1) ▪ 2002 (4.2)
Text
Wolfram Research (1996), Fibonacci, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Fibonacci.html (updated 2002).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1996. "Fibonacci." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2002. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Fibonacci.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1996). Fibonacci. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Fibonacci.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_fibonacci, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Fibonacci}", year="2002", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Fibonacci.html}", note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_fibonacci, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Fibonacci}, year={2002}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Fibonacci.html}, note=[Accessed: 24-February-2026]}