GaborFilter[data,r,k]
filters data by convolving with a Gabor kernel of pixel radius r and wave vector k.
GaborFilter[data,r,k,ϕ]
uses a Gabor kernel with phase shift ϕ.
GaborFilter[data,{r,σ},…]
uses a Gabor kernel with radius r and standard deviation σ.


GaborFilter
GaborFilter[data,r,k]
filters data by convolving with a Gabor kernel of pixel radius r and wave vector k.
GaborFilter[data,r,k,ϕ]
uses a Gabor kernel with phase shift ϕ.
GaborFilter[data,{r,σ},…]
uses a Gabor kernel with radius r and standard deviation σ.
Details and Options
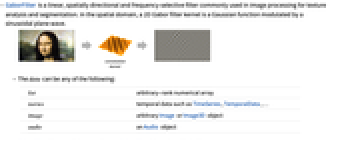
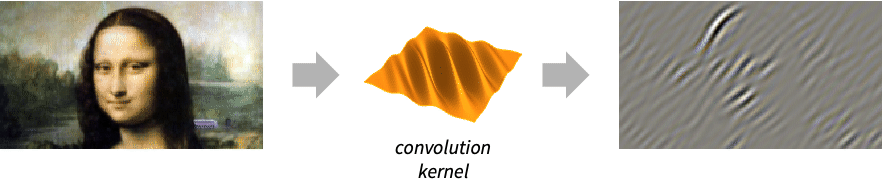
- GaborFilter is a linear, spatially directional and frequency-selective filter commonly used in image processing for texture analysis and segmentation. In the spatial domain, a 2D Gabor filter kernel is a Gaussian function modulated by a sinusoidal plane wave.
- The data can be any of the following:
-
list arbitrary-rank numerical array tseries temporal data such as TimeSeries, TemporalData, … image arbitrary Image or Image3D object audio an Audio object video a Video object - GaborFilter[data,r,k] is equivalent to GaborFilter[data,{r,r/2},k,0].
- Either of the r or σ can be lists, specifying different values for different directions.
- GaborFilter[image,…] by default gives an image of a real type of the same dimensions as image.
- The following options can be specified:
-
Padding "Fixed" padding method Standardized True whether to rescale the Gabor kernel to account for truncation WorkingPrecision Automatic the precision to use - With a setting Padding->None, GaborFilter[data,…] normally gives a result smaller than data.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (3)
Scope (8)
Data (5)
Options (6)
Padding (3)
WorkingPrecision (3)
MachinePrecision is by default used with integer arrays:
Perform exact computation instead:
With real arrays, by default the precision of the input is used:
WorkingPrecision is ignored when filtering images:
Applications (3)
Properties & Relations (5)
GaborFilter is equivalent to a convolution with a GaborMatrix:
Gabor filtering with a zero-valued wave vector is equivalent to Gaussian smoothing:
Impulse response of a Gabor filter:
Magnitude spectrum of the filter:
Gabor filtering of an image gives a real-valued image:
GaborFilter is a linear filter:
Related Guides
History
Introduced in 2012 (9.0) | Updated in 2014 (10.0) ▪ 2016 (11.0) ▪ 2025 (14.3)
Text
Wolfram Research (2012), GaborFilter, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GaborFilter.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2012. "GaborFilter." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GaborFilter.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2012). GaborFilter. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GaborFilter.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_gaborfilter, author="Wolfram Research", title="{GaborFilter}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GaborFilter.html}", note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_gaborfilter, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={GaborFilter}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GaborFilter.html}, note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}