Gudermannian[z]
gives the Gudermannian function ![]() .
.




Gudermannian
Gudermannian[z]
gives the Gudermannian function ![]() .
.
Details
- Mathematical function, suitable for both symbolic and numerical manipulation.
- The Gudermannian function is generically defined by
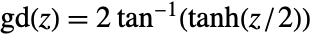 .
. - Gudermannian[z] has branch cut discontinuities in the complex
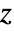 plane running from
plane running from 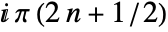 to
to 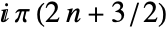 for integers
for integers 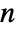 , where the function is continuous from the right.
, where the function is continuous from the right. - Gudermannian can be evaluated to arbitrary numerical precision.
- Gudermannian automatically threads over lists. »
- Gudermannian can be used with Interval and CenteredInterval objects. »
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (38)
Numerical Evaluation (6)
The precision of the output tracks the precision of the input:
Evaluate efficiently at high precision:
Compute the elementwise values of an array using automatic threading:
Or compute the matrix Gudermannian function using MatrixFunction:
Compute worst-case guaranteed intervals using Interval and CenteredInterval objects:
Or compute average-case statistical intervals using Around:
Specific Values (3)
Find a value of ![]() for which the
for which the ![]() using Solve:
using Solve:
Visualization (3)
Plot the Gudermannian function:
Plot the real part of Gudermannian[z]:
Plot the imaginary part of Gudermannian[z]:
Function Properties (11)
Gudermannian is defined for all real values:
Gudermannian is defined for all complex values except branch points:
Gudermannian has the mirror property ![]() :
:
Gudermannian is an odd function:
![]() is an analytic function of
is an analytic function of ![]() for real
for real ![]() :
:
It is neither analytic nor meromorphic in the complex plane:
Gudermannian is non-decreasing:
Gudermannian is injective:
Gudermannian is neither non-negative nor non-positive:
Gudermannian has no singularities or discontinuities:
Gudermannian is neither convex nor concave:
TraditionalForm formatting:
Differentiation (3)
Integration (4)
Compute the indefinite integral using Integrate:
The definite integral of Gudermannian over a period is 0:
Series Expansions (4)
Find the Taylor expansion using Series:
Plots of the first three approximations around ![]() :
:
The first-order Fourier series:
The Taylor expansion at a generic point:
Gudermannian can be applied to a power series:
Function Representations (4)
Gudermannian can be represented in terms of Exp and ArcTan on the real line:
Representation as an integral on the real line:
Since Gudermannian is odd, the same result is obtained for negative ![]() :
:
Gudermannian can be represented in terms of Tanh and ArcTan away from the imaginary axis:
This representation is invalid on the half that is further from the origin of each branch cut strip:
Represent Gudermannian using Piecewise:
This representation is correct at all points, including branch cuts:
Applications (3)
Properties & Relations (2)
Use FunctionExpand to expand Gudermannian in terms of elementary functions:
Use FullSimplify to prove identities involving the Gudermannian function:
See Also
Related Guides
Related Links
Text
Wolfram Research (2008), Gudermannian, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Gudermannian.html (updated 2020).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2008. "Gudermannian." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2020. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Gudermannian.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2008). Gudermannian. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Gudermannian.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_gudermannian, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Gudermannian}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Gudermannian.html}", note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_gudermannian, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Gudermannian}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Gudermannian.html}, note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}