HardcorePointProcess[μ,rh,d]
represents a hard-core point process with constant intensity μ and hard-core radius rh in ![]() .
.


HardcorePointProcess
HardcorePointProcess[μ,rh,d]
represents a hard-core point process with constant intensity μ and hard-core radius rh in ![]() .
.
Details


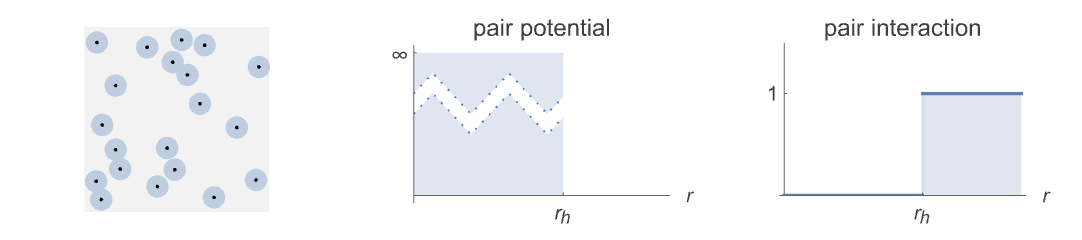
- HardcorePointProcess models point configurations where the points cannot be within a radius rh of each other but otherwise are uniformly distributed with intensity μ points per volume unit.
- The hard-core model is typically used when the underlying points behave like a collection of hard marbles, including things like gas molecules, metal deposits, sintered material and biological cells.
- The hard-core point process can be defined as a GibbsPointProcess in terms of its intensity μ and the pair potential
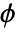 or pair interaction
or pair interaction 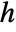 , which are both parametrized by rh as follows:
, which are both parametrized by rh as follows: -
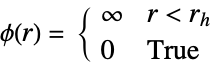
pair potential 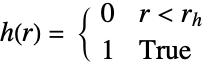
pair interaction - A point configuration
 from a hard-core point process HardcorePointProcess[μ,rh,d] in an observation region reg has density function
from a hard-core point process HardcorePointProcess[μ,rh,d] in an observation region reg has density function 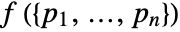 proportional to
proportional to ![mu^n product_(i!=j)Boole[||p_i-p_j||>r_(h)] mu^n product_(i!=j)Boole[||p_i-p_j||>r_(h)]](Files/HardcorePointProcess.en/9.png) with respect to PoissonPointProcess[1,d].
with respect to PoissonPointProcess[1,d]. - The Papangelou conditional density
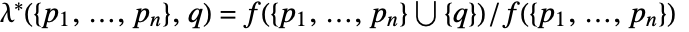 for adding a point
for adding a point 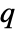 to a point configuration
to a point configuration  is
is ![mu product_iBoole[||p_i-q||>r_(h)] mu product_iBoole[||p_i-q||>r_(h)]](Files/HardcorePointProcess.en/13.png) .
. - HardcorePointProcess allows μ and rh to be any positive numbers, and d to be any positive integer.
- HardcorePointProcess is a special case of GibbsPointProcess and is equivalent to StraussPointProcess[μ, 0, rh].
- Possible Method settings in RandomPointConfiguration for HardcorePointProcess are:
-
"MCMC" MCMC birth and death "Exact" coupling from the past - Possible PointProcessEstimator settings in EstimatedPointProcess for HardcorePointProcess are:
-
Automatic automatically choose the parameter estimator "MaximumPseudoLikelihood" maximize the pseudo-likelihood - HardcorePointProcess can be used with such functions as RipleyK and RandomPointConfiguration.
Examples
open all close allBasic Examples (2)
Scope (3)
Options (4)
Method (4)
Simulate using the Markov chain Monte Carlo method:
Specify the number of recursive calls to the sampler:
Provide an initial state for the simulation:
The initial point must have nonzero density to ensure that the result is a valid configuration:
Check if the minimal distance between the points is smaller than the hard-core radius:
Related Guides
History
Text
Wolfram Research (2020), HardcorePointProcess, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HardcorePointProcess.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2020. "HardcorePointProcess." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HardcorePointProcess.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2020). HardcorePointProcess. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HardcorePointProcess.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_hardcorepointprocess, author="Wolfram Research", title="{HardcorePointProcess}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HardcorePointProcess.html}", note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_hardcorepointprocess, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={HardcorePointProcess}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/HardcorePointProcess.html}, note=[Accessed: 25-February-2026]}