RegionDimension
RegionDimension[reg]
gives the geometric dimension of the region reg.
Details and Options

- The geometric dimension d of reg is the largest d such that a d-dimensional ball can be completely embedded in the region.
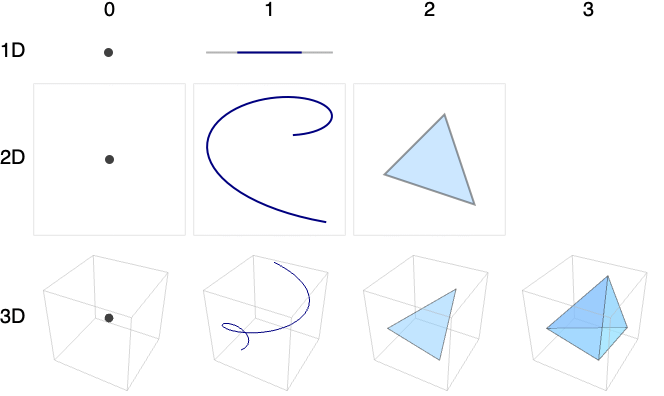
- Typical names for regions of different dimensions include:
-
0 points 1 lines, curves, arcs, segments, intervals 2 planes, surfaces 3 solids, volumes - Example cases with rows corresponding to embedding dimension and columns to RegionDimension:
- RegionDimension takes an Assumptions option that can be used to specify assumptions on parameters.
Examples
open allclose allBasic Examples (4)
Scope (17)
Special Regions (4)
Formula Regions (3)
The dimension of a disk represented as an ImplicitRegion:
The dimension of a disk represented as a ParametricRegion:
Using a rational parametrization of the disk:
ImplicitRegion can have several components of different dimension:
RegionDimension gives the largest dimension:
Mesh Regions (4)
The dimension of a BoundaryMeshRegion:
The dimension of a MeshRegion:
A MeshRegion can have components of different dimension:
The RegionDimension is the largest dimension:
Derived Regions (4)
The dimension of a RegionIntersection:
The dimension of a TransformedRegion:
The dimension of a RegionBoundary:
RegionBoundary for a full-dimensional region is less than the original dimension:
RegionDimension for an intersection can be less than the original dimensions:
Geographic Regions (2)
Polygons with GeoPosition:
Polygons with GeoPositionXYZ:
Polygons with GeoPositionENU:
Polygons with GeoGridPosition:
Applications (8)
A zero-dimensional object is a collection of points:
A one-dimensional object is a collection of curves:
A two-dimensional object is a collection of surfaces:
Use RegionDimension to tell the difference between a volume and a surface:
Regions may be visually identical:
Compute dimension of regions that cannot be visualized:
The unit for RegionMeasure is ![]() with
with ![]() the length unit and
the length unit and ![]() :
:
Compute the measure of each region:
Compare with the result from RegionMeasure:
Extract MeshRegion primitives by dimension using MeshPrimitives:
Select only full-dimensional primitives:
Properties & Relations (8)
RegionDimension gives the largest dimension among parts of varying dimension:
The RegionDimension is the largest dimension:
RegionEmbeddingDimension is the dimension of the space in which a region exists:
It is always greater than or equal to RegionDimension:
DimensionalMeshComponents separates a mesh in different dimensional parts:
RegionMeasure and RegionCentroid are dimension dependent:
Integration over a region is dimension dependent:
Since the dimension is 2, integration corresponds to a surface integral:
The RegionDimension of a RegionBoundary is one less than that of the input:
The RegionDimension of a RegionUnion is equal to the largest input dimension:
RegionDimension of a RegionIntersection is no larger than the smallest input dimension:
Text
Wolfram Research (2014), RegionDimension, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionDimension.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2014. "RegionDimension." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionDimension.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2014). RegionDimension. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/RegionDimension.html